JobRunr is a powerful, distributed background job processing library for Java and Kotlin. It integrates seamlessly with Spring Boot, allowing developers to execute jobs asynchronously with minimal configuration. A key feature of JobRunr is its ability to function with or without a database, making it highly flexible depending on project requirements.
This article will explore how to use JobRunr in Spring Boot in both modes: with a database for persistence and durability, and without a database for in-memory job execution. It covers only the free feature of JobRunr.
1. What is JobRunr?
JobRunr is a Java library for background processing and job scheduling. It allows developers to offload long-running or time-consuming tasks to a separate worker thread, ensuring the main application remains responsive.

Important: the jobrunr-spring-boot-starter-2 is removed since JobRunr v8. In JobRunr Pro, support is still available.
To add JobRunr to your Spring project, these are the steps you need to take:
Depending on your version of Spring Boot, add the jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter dependency to your project Configure JobRunr via the Spring application.properties file Inject the JobScheduler or JobRequestScheduler bean and use it to create background jobs! Do you want to create jobs that automatically participate in the transactions managed by Spring? Then checkout JobRunr Pro!
Key Features of JobRunr
- Asynchronous job execution
- Supports Spring Boot out of the box
- Can be used with or without a database
- Distributed job processing
- Retry mechanism for failed jobs
- User-friendly job dashboard
2. Setting Up JobRunr in Spring Boot
To use JobRunr in a Spring Boot application, developers must add the required dependencies.
Add JobRunr Dependency
Include the JobRunr starter dependency in your pom.xml:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jobrunr/jobrunr -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jobrunr</groupId>
<artifactId>jobrunr</artifactId>
<version>7.4.1</version>
</dependency>3. Using JobRunr Without a Database (In-Memory Mode)
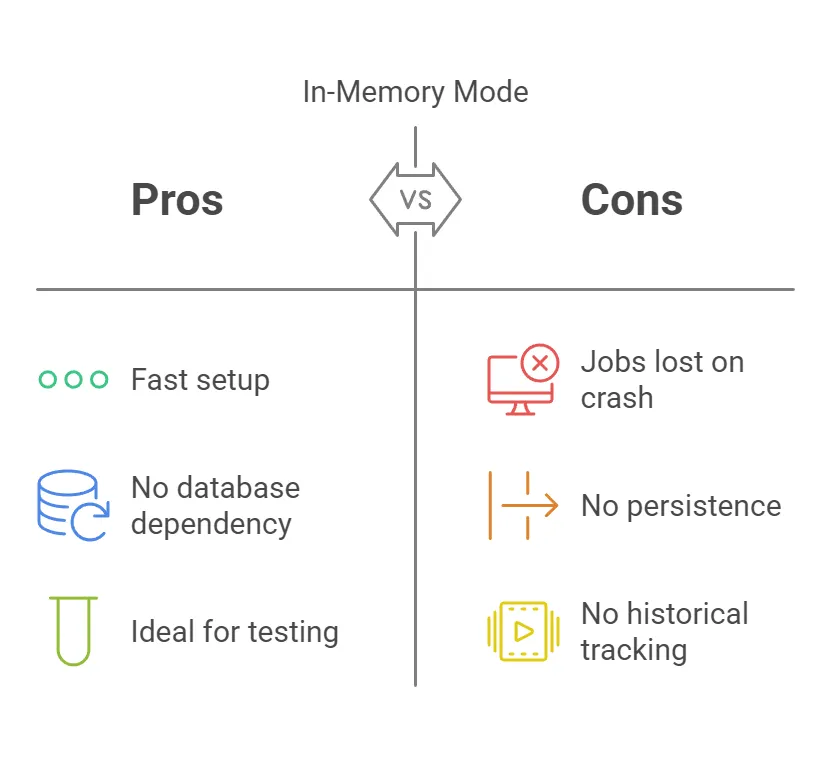
JobRunr supports an in-memory mode, which means jobs are not persisted and are lost when the application restarts. This mode is helpful for development, testing, or lightweight applications.
Configuring JobRunr Without a Database
By default, if no database is configured, JobRunr runs in-memory.
import org.jobrunr.configuration.JobRunr;
import org.jobrunr.scheduling.JobScheduler;
import org.jobrunr.storage.InMemoryStorageProvider;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class JobRunrConfig {
@Bean
public JobScheduler initJobRunr(InMemoryStorageProvider storageProvider) {
return JobRunr.configure()
.useStorageProvider(storageProvider)
.useBackgroundJobServer()
.useDashboard()
.initialize()
.getJobScheduler();
}
@Bean
public InMemoryStorageProvider storageProvider() {
return new InMemoryStorageProvider();
}
}Creating and Enqueuing a Job
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.jobrunr.scheduling.JobScheduler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
// Example service with a background job
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ExampleJobService {
public void performBackgroundTask(String taskData) {
log.info("Performing background task with data: {}", taskData);
// Simulate some work
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
log.info("Background task completed for: {}", taskData);
}
public void scheduleRecurringJob(JobScheduler jobScheduler) {
// Schedule a recurring job that runs every minute
jobScheduler.scheduleRecurrently(
"*/1 * * * *", // Cron expression (every minute for demonstration)
() -> performBackgroundTask("Recurring Task")
);
}
public void enqueueSimpleJob(JobScheduler jobScheduler) {
// Enqueue a one-time background job
jobScheduler.enqueue(() -> performBackgroundTask("One-time Task"));
}
}Creating a RESTful controller
import com.example.jobrunr.service.ExampleJobService;
import org.jobrunr.scheduling.JobScheduler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class JobController {
private final JobScheduler jobScheduler;
private final ExampleJobService jobService;
@Autowired
public JobController(JobScheduler jobScheduler, ExampleJobService jobService) {
this.jobScheduler = jobScheduler;
this.jobService = jobService;
}
@PostMapping("/trigger-job")
public ResponseEntity<String> triggerJob() {
// Enqueue a job
jobService.enqueueSimpleJob(jobScheduler);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Job enqueued successfully");
}
@PostMapping("/schedule-recurring-job")
public ResponseEntity<String> scheduleRecurringJob() {
// Schedule a recurring job
jobService.scheduleRecurringJob(jobScheduler);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Recurring job scheduled successfully");
}
}Pros and Cons of In-Memory Mode
4. Using JobRunr with a Database (Persistent Mode)
Database persistence is recommended for production applications to ensure jobs are not lost upon application restarts or crashes.

Important: you will need to add the correct dependency (jdbc-driver) for each of the databases below.
SQL databases Setting up an SQL database is easy-peasy because you probably don’t need to do a thing!
Sit back, relax and let JobRunr do the work for you! By default, JobRunr will automatically create the necessary tables for your database. Just like Liquibase and Flyway, it comes with a database migration manager that manages the database for you.
Supported Databases
JobRunr supports multiple databases, including:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- SQL Server
- H2 (for testing)
Set up PostgreSQL Database Server

Database Configuration in application.properties
For PostgreSQL:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/jobrunrdb spring.datasource.username=postgres spring.datasource.password=secret spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
Include the starter dependency in your pom.xml:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jobrunr/jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.jobrunr</groupId> <artifactId>jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter</artifactId> <version>7.4.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
Configuring JobRunr to Use the Database
@Configuration
public class JobRunrConfig {
@Bean
public JobScheduler initJobRunr(DataSource dataSource) {
return JobRunr.configure()
.useStorageProvider(new PostgresStorageProvider(dataSource, StorageProviderUtils.DatabaseOptions.CREATE))
.useBackgroundJobServer()
.useDashboard()
.initialize()
.getJobScheduler();
}
}Pros and Cons of Database Mode
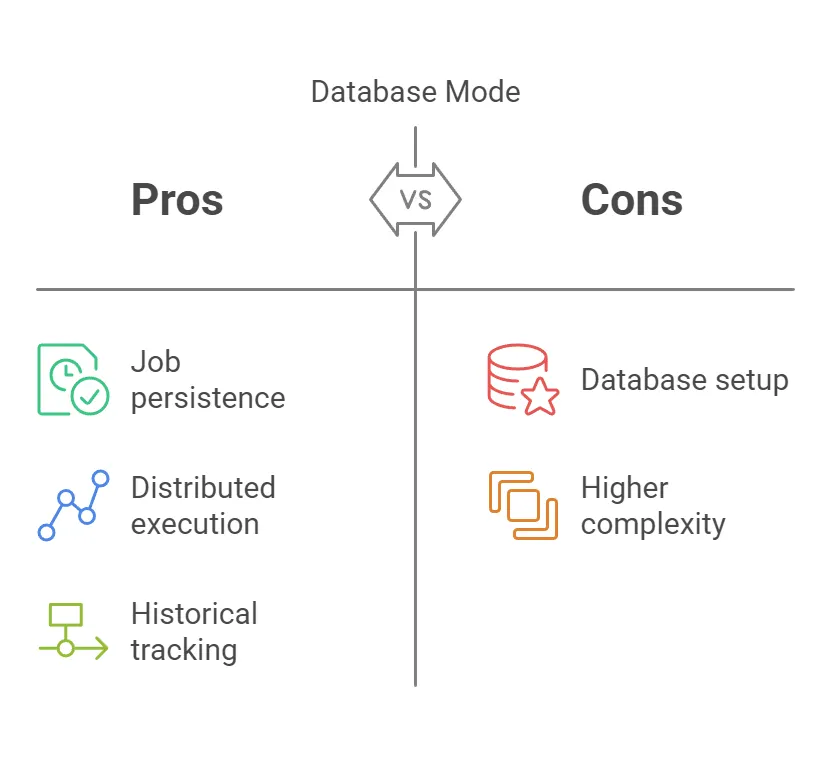
Table Jobrunr in Database

Example Query
-- Check background job servers SELECT * FROM public.jobrunr_backgroundjobservers; -- Check job status SELECT id, state, createdAt, scheduledAt FROM public.jobrunr_jobs ORDER BY createdAt DESC; -- Check recurring jobs SELECT id, cronExpression, nextRun FROM public.jobrunr_recurring_jobs; -- Check migrations SELECT * FROM public.jobrunr_migrations;
JobRunr Database Tables Explanation
1. public.jobrunr_backgroundjobservers This table tracks the background job servers in the system.
Columns:
idUnique identifier for each background job server instancenameName of the background job serverworker_pool_sizeNumber of worker threads in the job serversystem_total_memoryTotal system memory availablefree_memoryAvailable free memorymax_memoryMaximum memory allocationis_leaderBoolean indicating if this server is the leaderlast_hearthbeatTimestamp of the last heartbeat signalstarted_atTimestamp when the server was startedserver_statusCurrent status of the server (e.g., RUNNING, STOPPED)
2. public.jobrunr_jobs Stores all individual jobs processed by JobRunr.
Columns:
idUnique job identifierversionVersion number for optimistic lockingjob_signatureUnique signature of the job method and parametersstateCurrent state of the job (ENQUEUED, PROCESSING, SUCCEEDED, FAILED)created_atTimestamp when the job was createdupdated_atTimestamp of last updatescheduled_atScheduled execution timeenqueued_atTime when the job was enqueuedprocessing_atTime when the job started processingfailed_atTime of job failuresucceeded_atTime of successful job completionjob_jsonJSON representation of the job detailsjob_state_jsonJSON with detailed job state information
3. public.jobrunr_metadata Stores miscellaneous metadata for JobRunr.
Columns:
keyUnique identifier for the metadata entryvalueValue associated with the keycreated_at: Timestamp when metadata was createdupdated_at: Timestamp of last update
4. public.jobrunr_migrations Tracks database schema migrations for JobRunr.
Columns:
scriptName of the migration scriptexecuted_atTimestamp when the migration was executedsuccessBoolean indicating if migration was successfulscript_contentFull content of the migration script
5. public.jobrunr_recurring_jobs Stores information about recurring jobs.
Columns:
idUnique identifier for the recurring jobversionVersion for optimistic lockingjob_signatureSignature identifying the recurring job methodcronCron expression defining job recurrencenext_runTimestamp of the next scheduled job executioncreated_atTimestamp when the recurring job was createdupdated_atTimestamp of last updatejob_jsonJSON representation of the recurring job detailsstateCurrent state of the recurring job
Test JobRunr via Postman
POST to /trigger-job to enqueue a one-time job
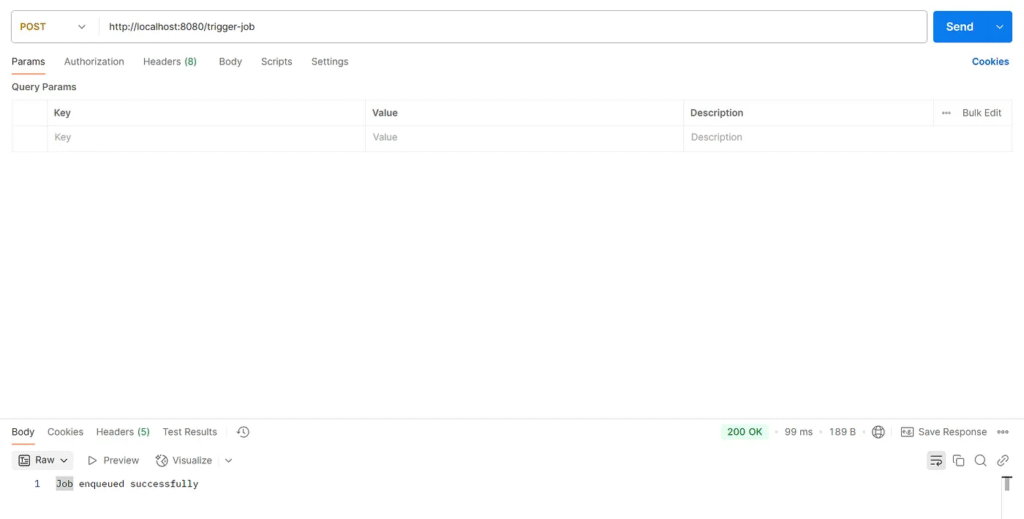
c.e.jobrunr.service.ExampleJobService : Performing background task with data: One-time Task c.e.jobrunr.service.ExampleJobService : Background task completed for: One-time Task
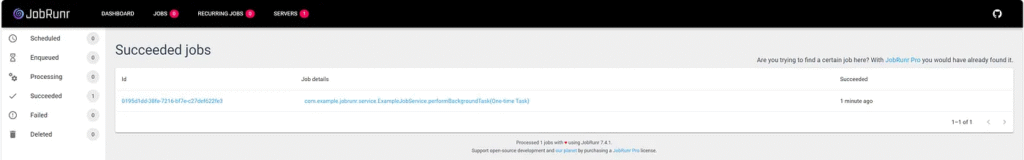
POST to /schedule-recurring-job to schedule a recurring job
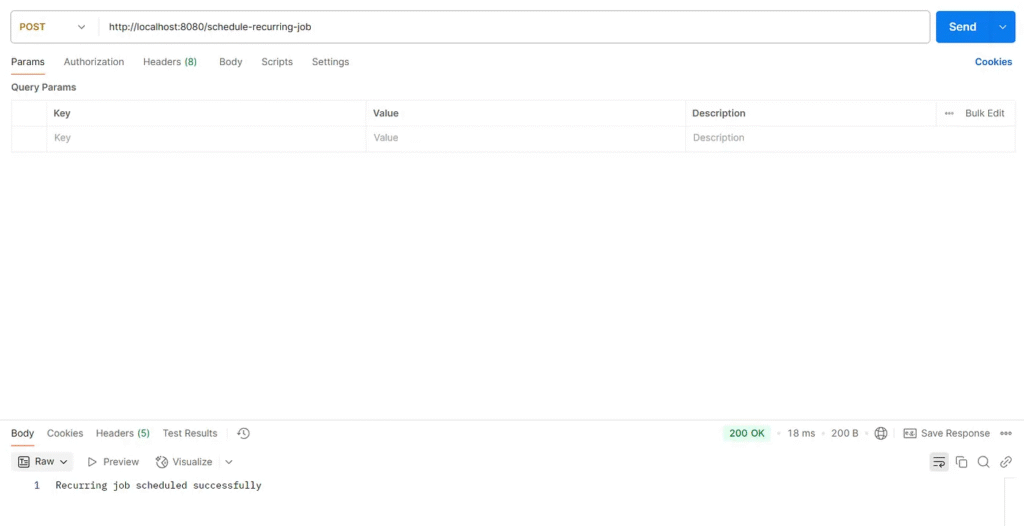
c.e.jobrunr.service.ExampleJobService : Performing background task with data: Recurring Task c.e.jobrunr.service.ExampleJobService : Background task completed for: Recurring Task
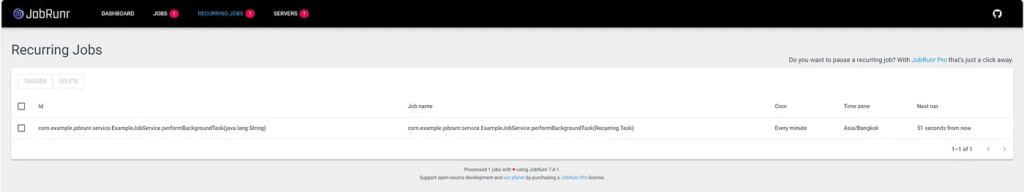
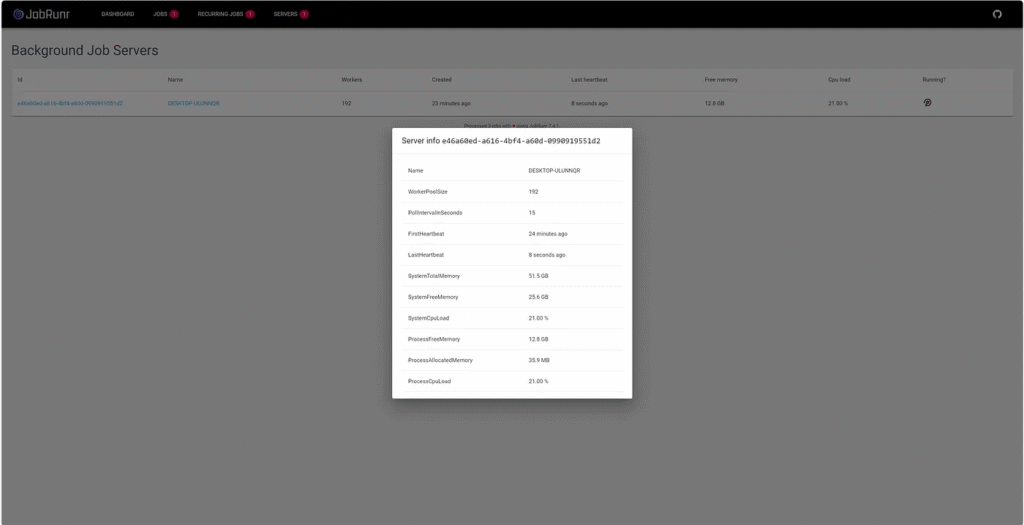
5. JobRunr Dashboard
One of JobRunr’s best features is its web-based dashboard that provides insights into job execution.
Enabling the Dashboard
Add this configuration application.properties:
jobrunr.dashboard.enabled=true jobrunr.dashboard.port=8000
Start the application and visit:
http://localhost:8000/
The JobRunr dashboard shows active, failed, and scheduled jobs.
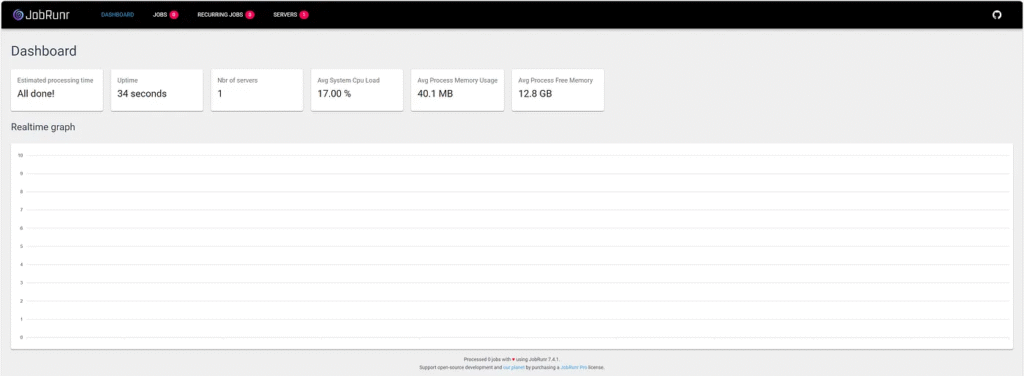
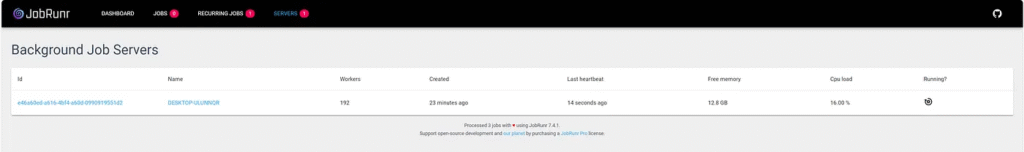
6. Scheduling Recurring Jobs
Developers can also schedule recurring jobs using JobRunr.
Example: Run a Job Every Hour
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RecurringJobService {
private final JobScheduler jobScheduler;
public RecurringJobService(JobScheduler jobScheduler) {
this.jobScheduler = jobScheduler;
}
@PostConstruct
public void scheduleRecurringJob() {
jobScheduler.scheduleRecurrently(Cron.hourly(), () -> log.info("Recurring job running..."));
}
}7. Handling Job Failures & Retries
JobRunr automatically retries failed jobs.
Example: Handling Exceptions in Jobs
@Service
public class FaultTolerantJobService {
private final JobScheduler jobScheduler;
public FaultTolerantJobService(JobScheduler jobScheduler) {
this.jobScheduler = jobScheduler;
}
public void scheduleFailingJob() {
jobScheduler.enqueue(() -> {
throw new RuntimeException("Simulating a job failure");
});
}
}JobRunr will retry the failed job up to 10 times before marking it as permanently failed.

JobRunr handles all exceptions that occur both in internal (belonging to JobRunr itself), and external methods (jobs, filters and so on), so it will not bring down the whole application. All internal exceptions are logged (so, don’t forget to enable logging) and in the worst case, background processing of a job will be stopped after 10 retry attempts with a smart exponential back-off policy.
JobRunr Pro
JobRunr Pro offers advanced features that enhance job processing, especially in production environments.

Why JobRunr Pro?
- JobRunr Pro’s advanced features can significantly improve reliability and performance for production environments with high numbers of jobs.
- The ability to define custom retry policies and batch jobs provides greater flexibility and control over job processing.
- The enhanced dashboard and dedicated support make monitoring and managing JobRunr in production more manageable.
Comparing JobRunr with Other Job Schedulers
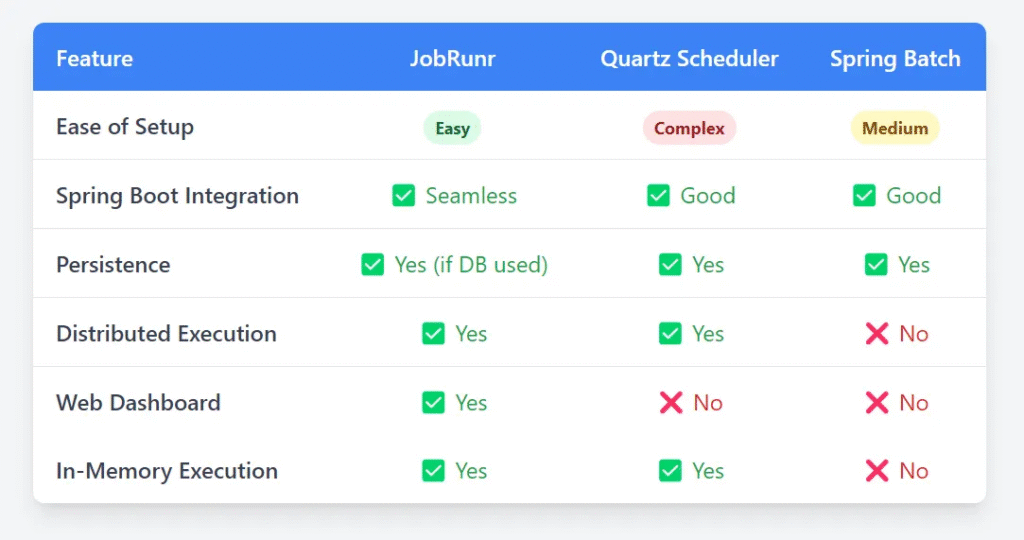
JobRunr stands out for its simplicity and seamless Spring Boot integration, making it an excellent choice for background job execution.
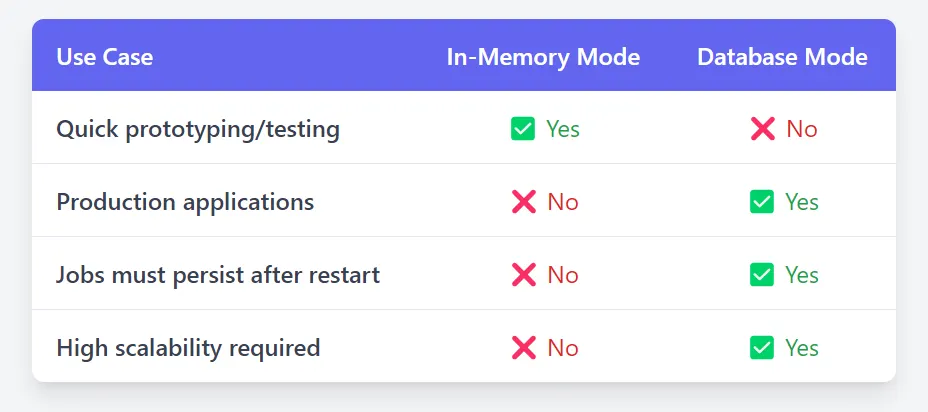
9. When to Use JobRunr Without vs. With a Database
10. Conclusion
JobRunr is a powerful, developer-friendly background job processing library for Spring Boot applications.
- Use in-memory mode for quick jobs and testing.
- Use database mode for production-grade applications with persistence.
- Take advantage of JobRunr’s dashboard for job monitoring.
Integrating JobRunr into your Spring Boot projects allows developers to manage background jobs with minimal effort.
This article was originally published on Medium.



