Java is a widely used programming language known for its platform independence, robustness, and security. One of the foundational concepts in Java programming is data types. Understanding Java data types is crucial because they define the size, type, and value range of variables in a program.
In this tutorial, we will cover:
- Primitive and non-primitive data types
- Type conversion and casting
- Best practices for using data types in Java
1. Primitive Data Types
Java provides eight built-in primitive data types, which store simple values and consume less memory.
1.1 Integer Data Types
These data types store whole numbers (both positive and negative) without decimals.
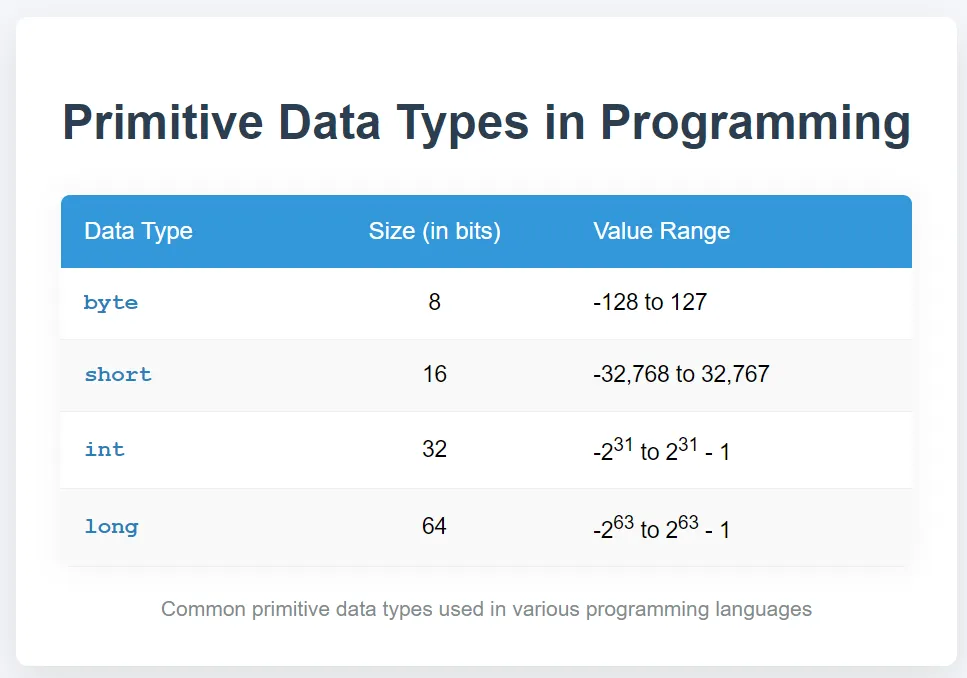
Example:
byte smallNumber = 100; short mediumNumber = 30000; int integerNumber = 123456789; long largeNumber = 1234567890123L; // 'L' denotes a long literal
1.2 Floating-Point Data Types
These data types store decimal values and are used for computations requiring precision.
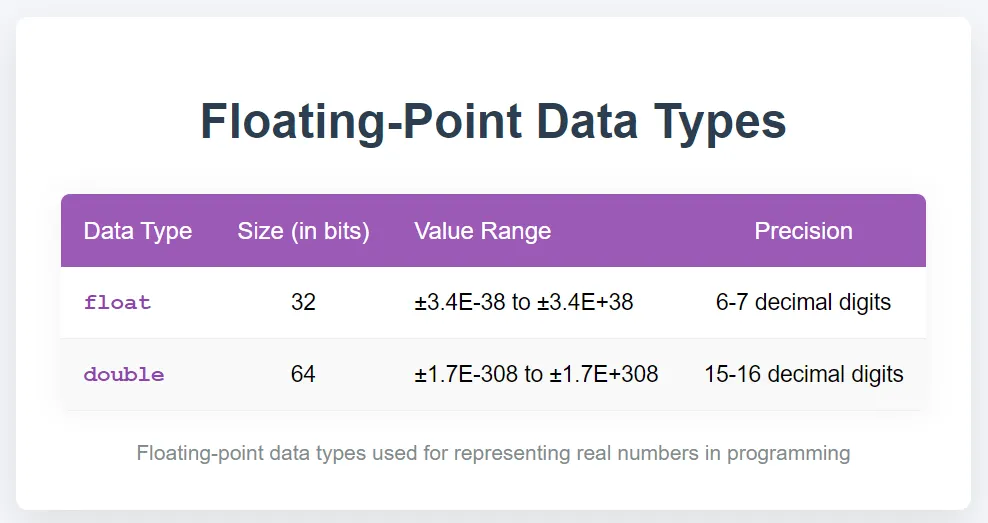
Example:
float price = 10.99f; // 'f' denotes a float literal double distance = 12345.6789; // Default for decimal numbers
1.3 Character Data Type
The char data type stores a single character using Unicode encoding.

Example:
char grade = 'A'; char symbol = '$'; char unicodeChar = '\u20AC'; // Unicode for Euro (€)
1.4 Boolean Data Type
The boolean data type represents one of two values: true or false.
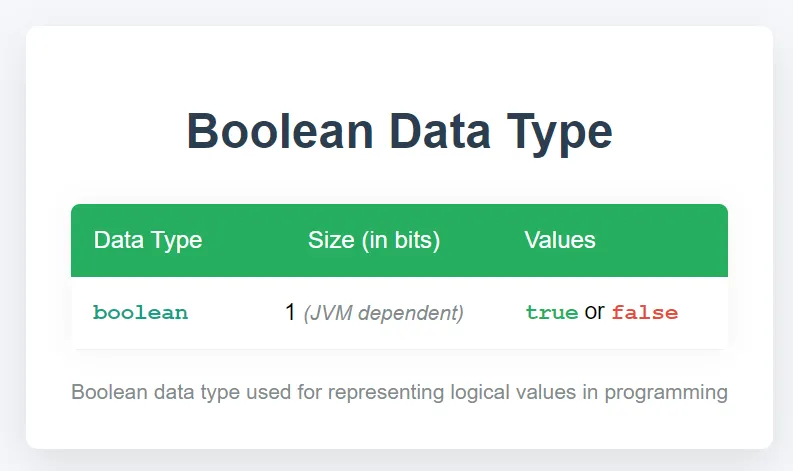
Example:
boolean isJavaFun = true; boolean isRainy = false;
2. Non-Primitive Data Types
Non-primitive data types are more complex and store references to memory locations rather than raw values.
2.1 Strings
A String is a sequence of characters and is immutable (cannot be changed after creation).
Example:
String message = "Hello, Java!";
2.2 Arrays
An array is a collection of elements of the same type.
Example:
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40};
String[] names = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"};2.3 Classes and Objects
Classes are blueprints for creating objects.
Example:
class Car {
String brand = "Toyota";
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car(); // Creating an object
System.out.println(myCar.brand);
}
}3. Type Conversion and Casting
Java supports implicit and explicit type conversion.
3.1 Implicit Type Conversion (Widening)
It happens automatically when converting a smaller data type to a larger one.
Example:
int num = 100; double bigNum = num; // Automatic conversion from int to double
3.2 Explicit Type Conversion (Narrowing)
Requires manual intervention when converting a larger data type to a smaller one.
Example:
double price = 9.99; int intPrice = (int) price; // Explicit casting from double to int
4. Wrapper Classes
Java provides wrapper classes for each primitive data type to allow them to be used as objects.
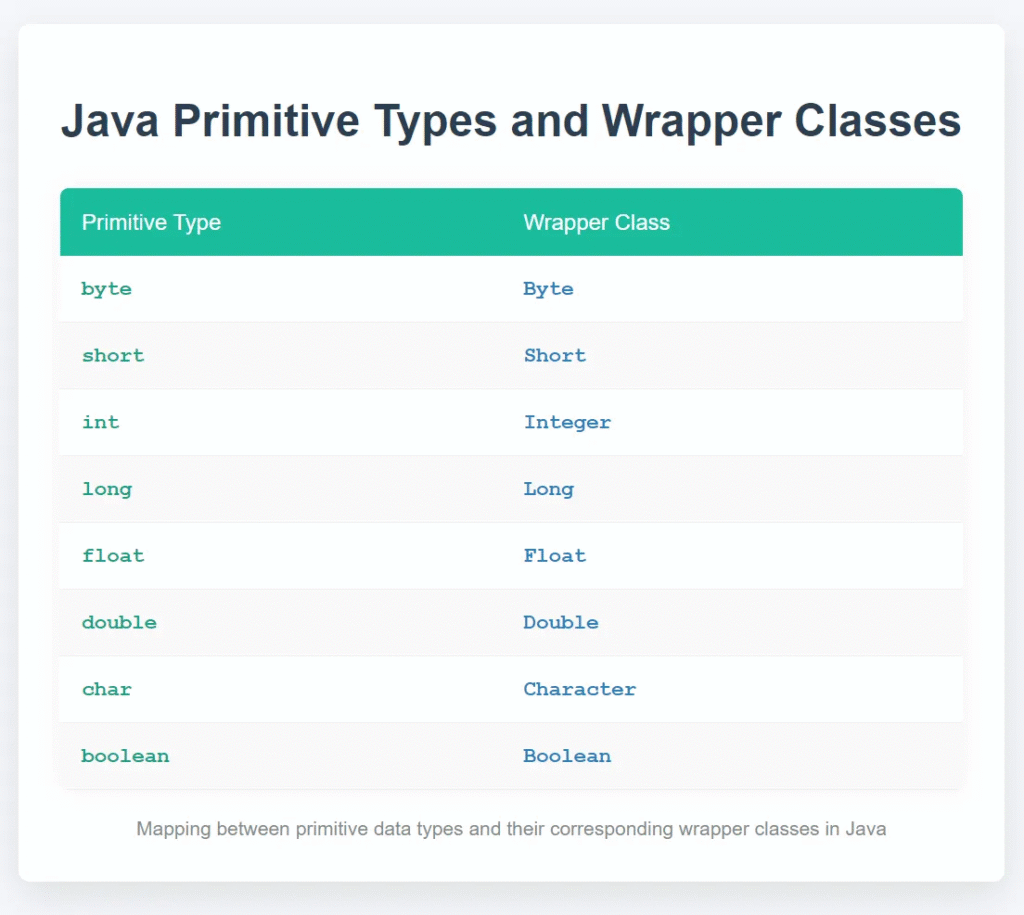
Example:
int num = 10; Integer wrappedNum = num; // Autoboxing int unwrappedNum = wrappedNum; // Unboxing
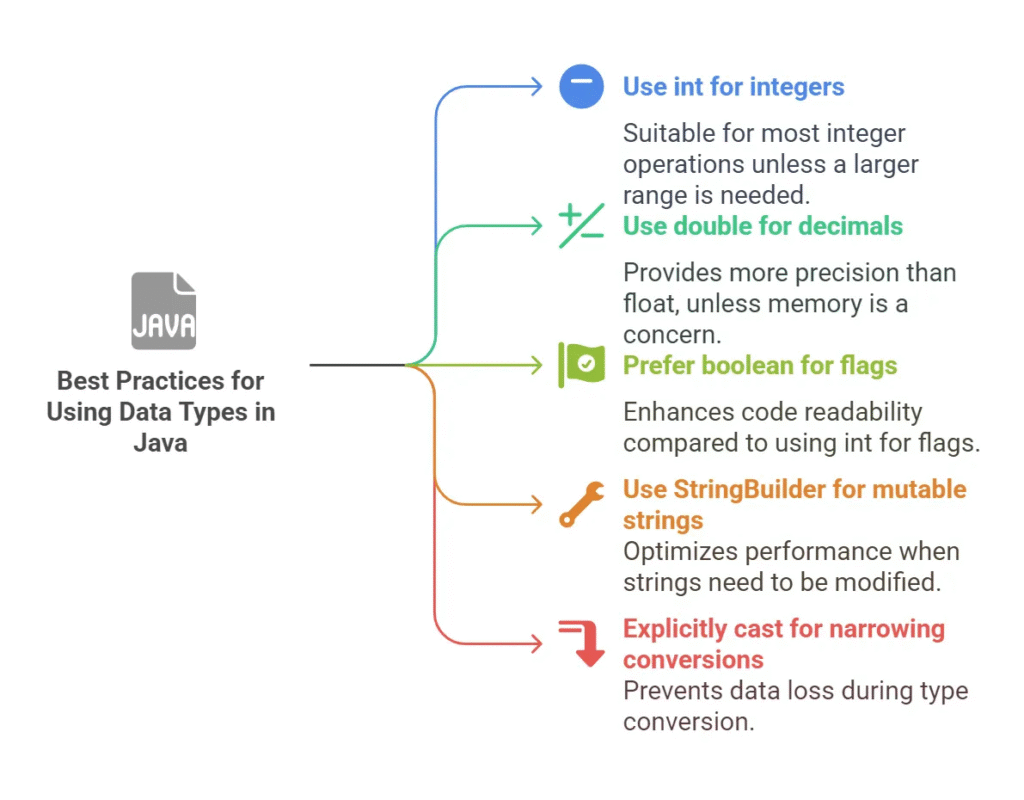
5. Best Practices for Using Data Types in Java
Conclusion
Understanding Java data types is fundamental for writing efficient programs. By mastering primitive and non-primitive types, type conversion, and wrapper classes, you can write better Java applications.



