Eureka is a service discovery server that is part of the Spring Cloud Netflix suite, which is based on Netflix’s Eureka. It allows microservices to register themselves as they appear in the system landscape and enable client-side load balancing.
Benefit.
Service Discovery:
Eureka Server allows services to register themselves and discover other services dynamically.
Health Checks and Status Monitoring
Eureka Server performs health checks on registered services.
Scalability and Flexibility
As services are scaled up or down, Eureka automatically updates the registry with the new instances or removes those no longer available.
Eureka server alternative.
Eureka Server is for service discovery in microservices architectures, but you might also consider several other tools and frameworks.
Kubernetes Service Discovery.
Kubernetes provides built-in service discovery as part of its orchestration capabilities.

It groups containers that make up an application into logical units for easy management and discovery. Kubernetes builds upon 15 years of experience of running production workloads at Google, combined with best-of-breed ideas and practices from the community.
Planet Scale Designed on the same principles that allow Google to run billions of containers a week, Kubernetes can scale without increasing your operations team.
ZooKeeper.
Apache ZooKeeper is a distributed coordination service that provides service discovery and configuration management.

AWS Service Discovery.
AWS provides a service discovery solution integrated with its ecosystem.

Use Case Scenario.
The software architecture design deploys the Spring Boot application on Docker. The application has multiple instances, each with its own port.
The software architecture used Eureka for each service registration in the Eureka server. Then, service discovery was used to get requests from the Eureka client using load balancing and RestTemplate.
Example of how to set up an Eureka Server and an Eureka Client using Spring Boot.
Directory structure.
/microservices-project │ ├── /eureka-server │ ├── /src │ │ ├── /main │ │ │ ├── /java │ │ │ │ └── /com │ │ │ │ └── /example │ │ │ │ └── /eureka_server │ │ │ │ └── EurekaServerApplication.java │ │ │ ├── /resources │ │ │ │ └── application.yml │ │ ├── Dockerfile │ │ └── pom.xml │ ├── /eureka-client │ ├── /src │ │ ├── /main │ │ │ ├── /java │ │ │ │ └── /com │ │ │ │ └── /example │ │ │ │ └── /eureka_client │ │ │ │ └── ClientService1Application.java │ │ │ ├── /resources │ │ │ │ └── application.yml │ │ ├── Dockerfile │ │ └── pom.xml │ ├── /service-discovery │ ├── /src │ │ ├── /main │ │ │ ├── /java │ │ │ │ └── /com │ │ │ │ └── /example │ │ │ │ └── /service_discovery │ │ │ │ └── ServiceConsumerController.java │ │ │ ├── /resources │ │ │ │ └── application.yml │ │ ├── Dockerfile │ │ └── pom.xml │ ├── docker-compose.yml
Setting Up Eureka Server.
1. The developer created the Eureka Server project
using spring initialzr
2. Add Maven dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>3. Make sure also to include the Spring Cloud dependency management.
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2023.0.3</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>4. Enable Eureka Server.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}5. Configure application.yml or application.properties
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90
server:
enableSelfPreservation: true # Make sure this is enabled for safety
evictionIntervalTimerInMs: 60000 # Frequency of eviction checks
renewalThreshold: 0.85 # Fraction of renewal threshold (default is 0.85)
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server6. To prevent this error. Config enables self-preservation, and expiration must be configured.
EMERGENCY! EUREKA MAY BE INCORRECTLY CLAIMING INSTANCES ARE UP WHEN THEY'RE NOT. RENEWALS ARE LESSER THAN THRESHOLD AND HENCE THE INSTANCES ARE NOT BEING EXPIRED JUST TO BE SAFE.

7. Eureka has a Self-Preservation Mode feature, which prevents instances from being removed from the registry in case of network partitions or when it perceives a high chance of false positives in instance status.
8. Create a Dockerfile.
# Stage 1: Build the JAR file FROM maven:3.9.7-amazoncorretto-21 AS build WORKDIR /app COPY pom.xml . COPY src ./src RUN mvn clean package -DskipTests # Stage 2: Run the application FROM amazoncorretto:21-alpine VOLUME /tmp COPY --from=build /app/target/*.jar eureka-server.jar ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/eureka-server.jar"]
9. Create a Docker compose.
version: '3.8'
services:
eureka-server:
build:
context: ./eureka-server
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: eureka-server
ports:
- "8761:8761"
networks:
- eureka-network
networks:
eureka-network:
driver: bridge10. Run the Docker compose command to start the Eureka Server.
>docker compose up -d
The -d flag in the docker-compose up -d Command stands for “detached mode.” When you run Docker Compose with the -d flag, the containers start in the background, allowing you to continue using the terminal.
11. Check for the Eureka server image on Docker.
>docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE eureka-eureka-server latest fa5f8ef23d1f 2 minutes ago 374MB
12. Check for the Eureka server container on Docker.
>docker container ls CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c001e488a86b eureka-eureka-server "java -jar /eureka-s…" 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes 0.0.0.0:8761->8761/tcp eureka-server
Check the Eureka Dashboard.
The developer can access the Eureka dashboard by going to http://localhost:8761.
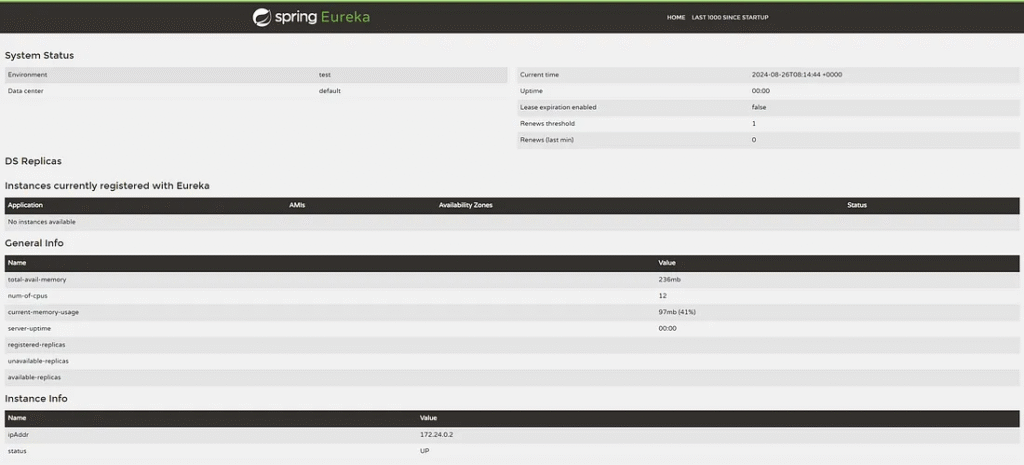
The dashboard shows information about the Eureka server and service register. It is ready for the client to register to the server.
Create Eureka Client.
The developer creates a client to register with the Eureka server. The developer can use Spring Initializr to create a new project.
Setting Up Eureka Client.
1. Add Maven dependencies.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Enable Eureka Client.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
}
}3. Create a HostNameController to check the service’s hostname.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HostNameController {
private Environment env;
@Autowired
public HostNameController(Environment env){
this.env = env;
}
@GetMapping(path = "/hostname")
public ResponseEntity<String> hostname(){
String hostname = env.getProperty("HOSTNAME"); //(container ID)
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(hostname);
}
}4. Configure application.yml
server:
port: 8081
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka-server:8761/eureka/
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30 # Frequency (in seconds) at which the client sends heartbeats to the Eureka server
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90 # Time (in seconds) after which the Eureka server considers the instance expired if no heartbeat is received
spring:
application:
name: eureka-clientAlternative, application.properties
# Server configuration server.port=8081 # Eureka client configuration eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka-server:8761/eureka/ # Eureka instance configuration eureka.instance.lease.expiration=90 # Spring application configuration spring.application.name=eureka-client
5. Create a Dockerfile.
# Stage 1: Build the JAR file FROM maven:3.9.7-amazoncorretto-21 AS build WORKDIR /app COPY pom.xml . COPY src ./src RUN mvn clean package -DskipTests # Stage 2: Run the application FROM amazoncorretto:21-alpine VOLUME /tmp COPY --from=build /app/target/*.jar eureka-client.jar ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/eureka-client.jar"]
6. Modify a Docker compose.
version: '3.8'
services:
eureka-server:
build:
context: ./eureka-server
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: eureka-server
ports:
- "8761:8761"
networks:
- eureka-network
eureka-client:
build:
context: ./eureka-client
dockerfile: Dockerfile
ports:
- "8080"
environment:
EUREKA_SERVER_URL: "http://eureka-server:8761/eureka/"
networks:
- eureka-network
deploy:
replicas: 3
networks:
eureka-network:
driver: bridge7. The developer wants to create multiple instances and add a replicas attribute. In this example, create three instances on port 8080.
8. Run the Docker compose command to start the Eureka Server and client.
>docker compose up -d
9. Check for the Eureka client image on Docker.
>docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE eureka-eureka-client latest 7e255f3122bf 53 minutes ago 364MB
10. Check for the Eureka client container on Docker.
>docker container ls CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2984cebfe8b7 eureka-eureka-client "java -jar /eureka-c…" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:6538->8080/tcp eureka-eureka-client-1 daff7d5d10cd eureka-eureka-client "java -jar /eureka-c…" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:6539->8080/tcp eureka-eureka-client-2 6394bc6099ae eureka-eureka-client "java -jar /eureka-c…" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:6541->8080/tcp eureka-eureka-client-3
11. The three instances have been created.
Check the Eureka Dashboard.
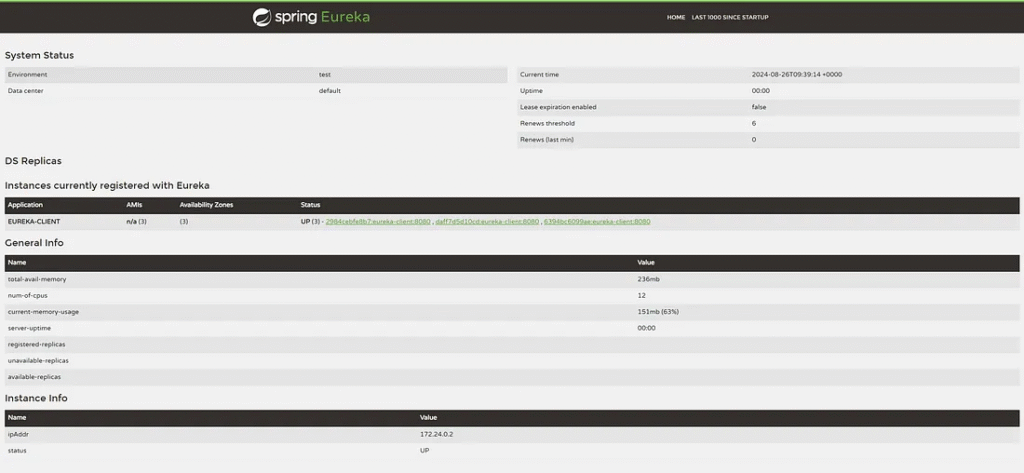
The Spring Boot application has been registered to the Eureka server.
Check the Spring Boot application status in the Eureka server.
http://localhost:8761/eureka/apps/EUREKA-CLIENT

Test Service Discovery and Communication.
The developer can test the Eureka client by using this service RestTemplate or WebClient with @LoadBalanced to discover and call the registered client service.
Create Service Discovery.
The developer creates a service discovery project to request from Eureka clients that register on the Eureka server. The developer can use Spring Initializr to create a new project.
Setting Up Service Discovery.
1. Configure @LoadBalanced RestTemplate.
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}2. Create RestController.
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class ServiceConsumerController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consume-service")
public String consumeService() {
String serviceUrl = "http://EUREKA-CLIENT:8080/hostname";
return restTemplate.getForObject(serviceUrl, String.class);
}
}3. Set the service port in an application properties file.
spring.application.name=service-discovery server.port=8081
4. Create a Dockerfile.
# Stage 1: Build the JAR file FROM maven:3.9.7-amazoncorretto-21 AS build WORKDIR /app COPY pom.xml . COPY src ./src RUN mvn clean package -DskipTests # Stage 2: Run the application FROM amazoncorretto:21-alpine VOLUME /tmp COPY --from=build /app/target/*.jar service-discovery.jar ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/service-discovery.jar"]
5. Modify Docker Compose.
version: '3.8'
services:
eureka-server:
build:
context: ./eureka-server
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: eureka-server
ports:
- "8761:8761"
networks:
- eureka-network
eureka-client:
build:
context: ./eureka-client
dockerfile: Dockerfile
ports:
- "8080"
environment:
EUREKA_SERVER_URL: "http://eureka-server:8761/eureka/"
networks:
- eureka-network
deploy:
replicas: 3
depends_on:
- eureka-server
service-discovery:
build:
context: ./service-discovery
dockerfile: Dockerfile
ports:
- "8081:8081"
networks:
- eureka-network
networks:
eureka-network:
driver: bridge6. Run the Docker compose command to start the service discovery server.
>docker compose up -d
7. Check for the Eureka client image on Docker.
>docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE eureka-service-discovery latest 0074c77004dd 16 minutes ago 338MB
8. Check for the Eureka client container on Docker.
>docker container ls CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 78b35e0eef42 eureka-service-discovery "java -jar /service-…" 16 minutes ago Up 16 minutes 0.0.0.0:8081->8081/tcp eureka-service-discovery-1
Test Service Discovery.
1. Execute the command to request service.
>curl http://localhost:8081/consume-service 2984cebfe8b7
2. Wait about a couple of minutes and send the request again.
>curl http://localhost:8081/consume-service 6394bc6099ae
3. The service discovery gets a request from a different client than the Eureka server. It proves that the hostname is different.
Conclusion
These steps ensure your Eureka Client is registered correctly and visible in the Eureka Server. Checking the Eureka dashboard, client logs, and Eureka REST API, and using service discovery with a consumer service will help verify that the registration process is functioning correctly.
Finally
Eureka is useful for developers who want to scale microservices.
The developer can use Spring Security to secure the Eureka server.
Eureka Server is a part of the Spring Cloud ecosystem and provides service discovery capabilities for microservices architectures. It works well with other components, such as OpenFeign and API Gateways.
This article was originally published on Medium.




