Creating PDF files is a common need in modern software. Reports, invoices, and certificates often require automated generation of PDFs. Java developers can achieve this easily using Apache PDFBox, a robust, open-source Java library for PDF manipulation.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn to install PDFBox, generate a simple PDF, add text, include images, apply fonts, create tables, and understand the license. Each step is simple yet powerful. By the end, you’ll have the confidence to build your own dynamic PDF solutions.
1. Introduction to Apache PDFBox
Apache PDFBox is an open-source Java library maintained by the Apache Software Foundation. It lets developers create, read, and manipulate PDF documents programmatically. Its strength lies in simplicity and flexibility.
The library supports operations like:
- Creating PDFs from scratch
- Extracting text from existing PDFs
- Merging and splitting PDF files
- Adding images, tables, and custom fonts
Beginners love PDFBox because it uses straightforward Java code. You don’t need advanced knowledge to start. A few lines of code can produce your first PDF document.
Apache PDFBox’s design follows object-oriented principles, making it intuitive for anyone familiar with Java basics.
You’ll soon see why it’s one of the most trusted tools in Java’s ecosystem.
2. Setting Up Apache PDFBox
Before coding, you must add PDFBox to your Java project. The easiest method is via Maven. Maven automatically manages your dependencies and keeps libraries up to date.
Add the Maven Dependency
Place the following snippet inside your pom.xml:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.pdfbox/pdfbox -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.pdfbox</groupId>
<artifactId>pdfbox</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>Verify Installation
After saving the configuration, refresh your project in the IDE. Maven will download the dependency automatically.
You’re ready to start coding. Keep your Java version at version 8 or higher for optimal compatibility.
With setup complete, let’s create your first PDF.
3. Creating Your First PDF File
Creating a PDF with PDFBox is a straightforward process that requires only a few steps. You make a document, add a page, and write content.
Here’s the minimal code example:
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDDocument;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDPage;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDPageContentStream;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.font.PDFont;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.font.PDType1Font;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.font.Standard14Fonts;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CreatePDF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (PDDocument document = new PDDocument()) {
PDPage page = new PDPage();
document.addPage(page);
PDPageContentStream content = new PDPageContentStream(document, page);
content.beginText();
PDFont font = new PDType1Font(Standard14Fonts.FontName.TIMES_ROMAN);
content.setFont(font, 18);
content.newLineAtOffset(100, 700);
content.showText("Hello, PDFBox!");
content.endText();
content.close();
document.save("FirstPDF.pdf");
System.out.println("PDF created successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}This code generates a PDF with the text “Hello, PDFBox!” in Helvetica Bold.
Each step is intuitive:
- Create a document.
- Add a page.
- Write text content.
- Save the document.
The library handles file streams safely, and the try-with-resources block ensures clean resource management.
You’ve now created your first PDF programmatically — an exciting milestone for any developer!
4. Adding Custom Fonts and Styles
Text styling enhances the elegance and readability of your PDFs. Apache PDFBox supports built-in and external fonts.
Using Built-In Fonts
PDFBox includes standard fonts like:
- Helvetica
- Times Roman
- Courier
Example:
PDFont font = new PDType1Font(Standard14Fonts.FontName.HELVETICA); content.setFont(font, 18);
Using External Fonts
You can also use custom fonts (.ttf files).
PDType0Font customFont = PDType0Font.load(document, new File("fonts/Roboto-Regular.ttf"));
content.setFont(customFont, 14);Custom fonts ensure your PDFs align with your brand’s design. Remember to embed fonts inside the PDF for portability.
You can also adjust font color:
float r = 50 / 255.0f; float g = 50 / 255.0f; float b = 200 / 255.0f; content.setNonStrokingColor(r, g, b);
This line applies a pleasant blue shade to your text. Combined with layout control, it allows professional-grade designs.
Typography matters because clear text enhances presentation and credibility. Keep your styles consistent and legible.
5. Adding Images to the PDF
PDFBox allows you to add images in formats like JPEG and PNG. Images elevate your PDFs and convey information visually.
Here’s how to add an image:
PDPageContentStream content = new PDPageContentStream(document, page);
PDImageXObject image = PDImageXObject.createFromFile("logo.jpg", document);
content.drawImage(image, 100, 550, 150, 100);
content.close();This snippet draws your image at coordinates (100, 550) with specified width and height.
Ensure your image file is located in the same directory or provide an absolute path to it.
To add multiple images, repeat drawImage() with different positions.
You can also overlay text above images for headers or captions.
Images in PDFs enhance visual storytelling, improve understanding, and make reports more engaging.
6. Creating Paragraphs and Wrapping Text
A real-world PDF often contains multiple lines and paragraphs. To handle text wrapping, you can manually control line breaks or create helper functions.
Here’s a basic approach:
String text = "Apache PDFBox makes PDF generation simple. You can easily create structured documents with Java.";
content.beginText();
PDType0Font customFont = PDType0Font.load(document, new File("Roboto-Regular.ttf"));
content.setFont(customFont, 12);
content.newLineAtOffset(50, 700);
float leading = 14.5f;
for (String line : text.split("\\. ")) {
content.showText(line.trim() + ".");
content.newLineAtOffset(0, -leading);
}
content.endText();This method writes paragraph text with manual wrapping. For long paragraphs, measure text width using PDType1Font.getStringWidth() and split lines accordingly.
Readable paragraphs improve your document’s professional appearance. Consistent spacing, margins, and alignment create polished results.
7. Creating Tables in a PDF
Tables structure data clearly and professionally. Apache PDFBox doesn’t provide built-in table utilities, but you can draw them manually using lines and text.
Example:
import java.awt.Color;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.common.PDRectangle;
float margin = 50;
float yStart = 700;
float rowHeight = 20;
float tableWidth = PDRectangle.LETTER.getWidth() - 2 * margin;
float colWidth = tableWidth / 3;
content.setStrokingColor(Color.BLACK);
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
content.moveTo(margin, yStart - i * rowHeight);
content.lineTo(margin + tableWidth, yStart - i * rowHeight);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
content.moveTo(margin + i * colWidth, yStart);
content.lineTo(margin + i * colWidth, yStart - 5 * rowHeight);
}
content.stroke();Add text to cells with showText() and position adjustments.
Although manual, this approach gives you complete control over layout, border thickness, and color.
Tables in PDFs make numerical data, invoices, and summaries look professional and transparent.
8. Handling Multiple Pages
Documents often require several pages. PDFBox simplifies this process by letting you add pages dynamically.
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
PDPage newPage = new PDPage();
document.addPage(newPage);
PDPageContentStream newContent = new PDPageContentStream(document, newPage);
newContent.beginText();
PDType0Font customFont = PDType0Font.load(document, new File("Roboto-Regular.ttf"));
newContent.setFont(customFont, 16);
newContent.newLineAtOffset(100, 700);
newContent.showText("This is page " + i);
newContent.endText();
newContent.close();
}This loop creates three pages with numbered headers.
Dynamic pagination enables reports and books where page counts vary according to the data.
Maintain consistent formatting and margins throughout the pages for visual harmony.
9. Understanding the Apache License 2.0
Apache PDFBox is distributed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive open-source license. It allows you to use, modify, and distribute the software freely — even in commercial projects.
Key Points
- You must include a copy of the license in your distribution.
- You can modify the code, but you must document your changes.
- There’s no warranty; you use it at your own risk.
This license promotes collaboration and innovation. It protects both developers and users while encouraging widespread adoption.
Always respect open-source licenses. They enable you to stand on the shoulders of global contributors.
Full license details are available here:

reliable and long-lived software products through collaborative, open-source software development.
10. Conclusion and Next Steps
You’ve learned to create, customize, and style PDFs using Apache PDFBox. You installed the library, added text, styled fonts, embedded images, built paragraphs, drew tables, and managed pages.
This journey shows how accessible document generation can be for Java beginners.
Now, explore advanced features such as:
- Adding hyperlinks
- Extracting text from existing PDFs
- Encrypting or signing documents
The more you experiment, the more proficient you become. Practice regularly and challenge yourself to automate real-world document workflows.
Success in programming comes from curiosity and persistence. Continue building, refining, and learning.
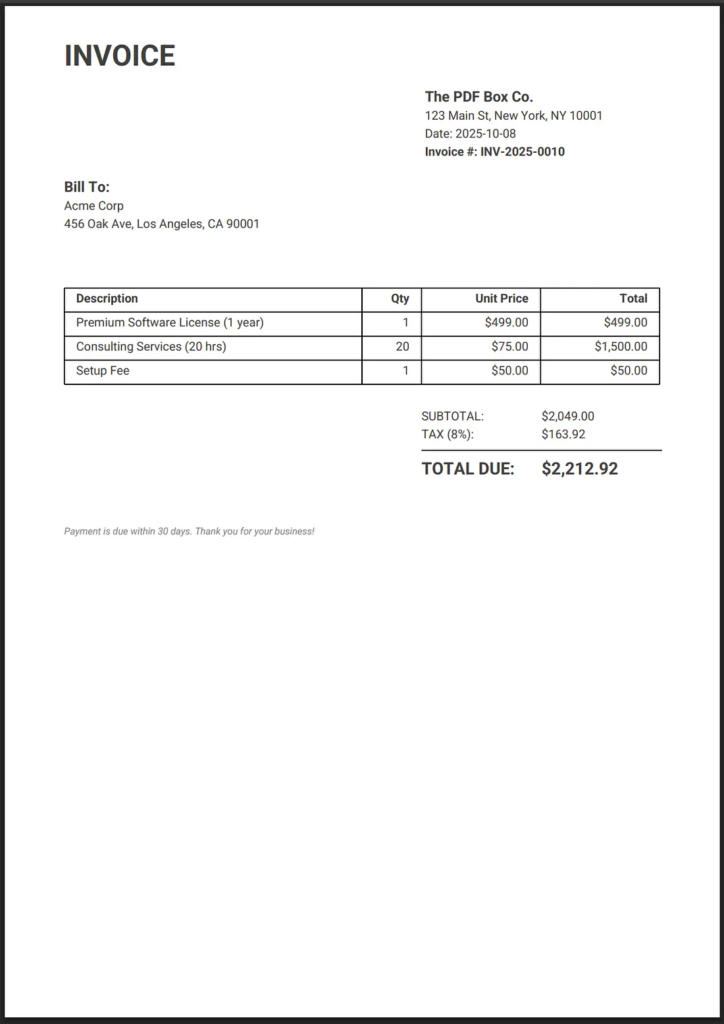
Java Code for Simple Invoice
This example defines helper methods to simplify text writing and manually draws the table structure.
package com.example.x_analytics;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDDocument;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDPage;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDPageContentStream;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.common.PDRectangle;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.font.*;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class SimplePdfboxInvoice {
// --- Invoice Data Structures ---
private static class InvoiceItem {
String description;
int quantity;
double unitPrice;
public InvoiceItem(String description, int quantity, double unitPrice) {
this.description = description;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
public double getTotal() {
return quantity * unitPrice;
}
}
// --- Document Setup Constants ---
private static final PDRectangle PAGE_SIZE = PDRectangle.A4;
private static final float MARGIN = 50;
private static final float CONTENT_WIDTH = PAGE_SIZE.getWidth() - 2 * MARGIN;
private static final String FONT_PATH_REGULAR = "Roboto-Regular.ttf";
private static final String FONT_PATH_BOLD = "Roboto-Bold.ttf";
private static final String FONT_PATH_ITALIC = "Roboto-Italic.ttf";
private static PDFont fontBold;
private static PDFont fontRegular;
private static PDFont fontItalic;
private static void loadCustomFonts(PDDocument document) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Loading custom fonts...");
// Load the font files into the PDDocument
fontRegular = PDType0Font.load(document, new File(FONT_PATH_REGULAR));
fontBold = PDType0Font.load(document, new File(FONT_PATH_BOLD));
fontItalic = PDType0Font.load(document, new File(FONT_PATH_ITALIC));
System.out.println("Custom fonts loaded.");
}
// --- Helper for Writing Text ---
private static void writeText(PDPageContentStream contentStream, PDFont font, float fontSize, float x, float y, String text) throws IOException {
contentStream.beginText();
contentStream.setFont(font, fontSize);
contentStream.newLineAtOffset(x, y);
contentStream.showText(text);
contentStream.endText();
}
// --- Corrected Table Drawing Helper ---
private static void drawTable(PDPageContentStream contentStream, float startY, float[] columnWidths, String[][] data, float rowHeight) throws IOException {
final int rows = data.length;
final int cols = columnWidths.length;
final float tableWidth = CONTENT_WIDTH;
float nextY = startY;
final float tableStart_X = MARGIN;
final float cellMargin = 10f;
// 1. Draw all horizontal lines (using moveTo/lineTo/stroke)
for (int i = 0; i <= rows; i++) {
contentStream.moveTo(tableStart_X, nextY);
contentStream.lineTo(tableStart_X + tableWidth, nextY);
contentStream.stroke();
if (i < rows) {
nextY -= rowHeight;
}
}
// 2. Draw all vertical lines (using moveTo/lineTo/stroke)
float currentX = tableStart_X;
for (float columnWidth : columnWidths) {
contentStream.moveTo(currentX, startY);
contentStream.lineTo(currentX, startY - rows * rowHeight);
contentStream.stroke();
currentX += columnWidth;
}
// Draw the rightmost vertical line
contentStream.moveTo(tableStart_X + tableWidth, startY);
contentStream.lineTo(tableStart_X + tableWidth, startY - rows * rowHeight);
contentStream.stroke();
// 3. Populate cells
float textX, textY;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
// Calculate text Y position (center vertically)
// Added adjustment (5f) for vertical centering
textY = startY - (i + 1) * rowHeight + rowHeight - cellMargin - 2;
// Calculate text X positions and write content
float xOffset = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
currentX = tableStart_X + xOffset;
String cellText = data[i][j];
PDFont cellFont = (i == 0) ? fontBold : fontRegular;
float fontSize = 10;
// Simple justification for some columns (using a fixed margin)
if (j == cols - 1 || j == cols - 2 || j == cols - 3) { // Last 3 columns (Qty, Price, Total)
float textWidth = cellFont.getStringWidth(cellText) / 1000 * fontSize;
textX = currentX + columnWidths[j] - textWidth - cellMargin;
} else { // Left-justified (Description)
textX = currentX + cellMargin;
}
writeText(contentStream, cellFont, fontSize, textX, textY, cellText);
xOffset += columnWidths[j];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- MOCK INVOICE DATA ---
String invoiceNo = "INV-2025-0010";
String invoiceDate = LocalDate.now().toString();
String companyName = "The PDF Box Co.";
String companyAddress = "123 Main St, New York, NY 10001";
String clientName = "Acme Corp";
String clientAddress = "456 Oak Ave, Los Angeles, CA 90001";
InvoiceItem[] items = new InvoiceItem[] {
new InvoiceItem("Premium Software License (1 year)", 1, 499.00),
new InvoiceItem("Consulting Services (20 hrs)", 20, 75.00),
new InvoiceItem("Setup Fee", 1, 50.00)
};
double subTotal = 0;
for (InvoiceItem item : items) {
subTotal += item.getTotal();
}
double taxRate = 0.08; // 8% tax
double taxAmount = subTotal * taxRate;
double grandTotal = subTotal + taxAmount;
DecimalFormat currencyFormat = new DecimalFormat("#,##0.00");
String outputFileName = "D:\\logs\\pdf\\SimpleInvoice.pdf";
// --- PDFBox Generation ---
try (PDDocument document = new PDDocument()) {
PDPage page = new PDPage(PAGE_SIZE);
document.addPage(page);
loadCustomFonts(document);
try (PDPageContentStream contentStream = new PDPageContentStream(document, page)) {
float currentY = PAGE_SIZE.getHeight() - MARGIN;
// 1. INVOICE TITLE
contentStream.setNonStrokingColor(Color.DARK_GRAY);
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 24, MARGIN, currentY, "INVOICE");
currentY -= 30;
// 2. COMPANY DETAILS (Right Side)
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 12, MARGIN + 300, currentY, companyName);
currentY -= 15;
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, MARGIN + 300, currentY, companyAddress);
currentY -= 15;
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, MARGIN + 300, currentY, "Date: " + invoiceDate);
currentY -= 15;
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 10, MARGIN + 300, currentY, "Invoice #: " + invoiceNo);
currentY -= 30;
// 3. BILLING ADDRESS (Left Side)
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 12, MARGIN, currentY, "Bill To:");
currentY -= 15;
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, MARGIN, currentY, clientName);
currentY -= 15;
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, MARGIN, currentY, clientAddress);
currentY -= 50;
// 4. INVOICE ITEMS TABLE
// Table Headers
String[] headers = {"Description", "Qty", "Unit Price", "Total"};
// Item Data Rows
String[][] tableData = new String[items.length + 1][headers.length];
tableData[0] = headers; // First row is the header
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
tableData[i+1] = new String[] {
items[i].description,
String.valueOf(items[i].quantity),
"$" + currencyFormat.format(items[i].unitPrice),
"$" + currencyFormat.format(items[i].getTotal())
};
}
float rowHeight = 20;
float[] columnWidths = {
CONTENT_WIDTH * 0.50f, // Description: 50%
CONTENT_WIDTH * 0.10f, // Qty: 10%
CONTENT_WIDTH * 0.20f, // Unit Price: 20%
CONTENT_WIDTH * 0.20f // Total: 20%
};
// Draw the table
contentStream.setLineWidth(1f);
contentStream.setStrokingColor(Color.BLACK);
drawTable(contentStream, currentY, columnWidths, tableData, rowHeight);
// Update Y position after the table
currentY -= (items.length + 1) * rowHeight + 30;
// 5. SUMMARY (Right Side Alignment)
float summaryX = MARGIN + CONTENT_WIDTH * 0.60f; // Start summary columns at 60% of width
// Subtotal
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, summaryX, currentY, "SUBTOTAL:");
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, summaryX + 100, currentY, "$" + currencyFormat.format(subTotal));
currentY -= 15;
// Tax
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, summaryX, currentY, "TAX (" + (int)(taxRate * 100) + "%):");
writeText(contentStream, fontRegular, 10, summaryX + 100, currentY, "$" + currencyFormat.format(taxAmount));
currentY -= 10;
// GRAND TOTAL (Bold and Larger)
contentStream.setLineWidth(1f);
// Using moveTo/lineTo/stroke for the separator line
contentStream.moveTo(summaryX, currentY);
contentStream.lineTo(summaryX + 200, currentY);
contentStream.stroke();
currentY -= 20;
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 14, summaryX, currentY, "TOTAL DUE:");
writeText(contentStream, fontBold, 14, summaryX + 100, currentY, "$" + currencyFormat.format(grandTotal));
currentY -= 50;
// 6. Footer Notes
contentStream.setNonStrokingColor(Color.GRAY);
writeText(contentStream, fontItalic, 8, MARGIN, currentY, "Payment is due within 30 days. Thank you for your business!");
} // contentStream closes automatically here
document.save(outputFileName);
System.out.println("Invoice created successfully: " + outputFileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Key Takeaways
- Apache PDFBox simplifies the creation and manipulation of PDFs in Java.
- You can create rich documents with text, images, fonts, and tables.
- Installation via Maven makes setup effortless.
- The Apache License 2.0 allows commercial and open-source use.
- Consistency and clarity in layout lead to professional results.
- Practice is the key to mastering PDFBox and Java automation.
Finally
Every great developer starts small. Your first “Hello, PDFBox” program is the foundation for powerful document automation in Java. Keep going — your skills will grow with every page you create.
This article was originally published on Medium.



