Apache Kafka is a powerful distributed event streaming platform widely used for building real-time data pipelines and event-driven architectures. Spring Boot, on the other hand, simplifies Java development by providing an opinionated framework with built-in support for Kafka integration. This article will guide you through integrating a Spring Boot application with an Apache Kafka server, covering setup, producer and consumer configurations, and best practices.
1. Understanding Kafka and Spring Boot Integration
Kafka operates as a messaging system that handles large streams of data efficiently. It consists of:
- Producers: Applications that publish messages to Kafka topics.
- Consumers: Applications that subscribe to Kafka topics and process messages.
- Brokers: Kafka servers that manage data storage and message distribution.
- Topics & Partitions: Messages are categorized into topics, which can be partitioned for scalability.
Spring Boot provides seamless integration with Kafka through the spring-kafka module, allowing developers to produce and consume messages easily.
2. Setting Up Apache Kafka
Before integrating with Spring Boot, we need to set up a Kafka server.

3. Creating a Spring Boot Kafka Project
We need to set up a project to integrate Kafka with Spring Boot.
Step 1: Create a Spring Boot Project
Use Spring Initializr to generate a new project with the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring for Apache Kafka
Step 2: Add Kafka Dependencies
Add the following dependencies to pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
</dependency>4. Configuring Kafka in Spring Boot
Spring Boot simplifies Kafka configuration by providing built-in properties.
Define Kafka Configuration in application.yml
spring:
kafka:
producer:
bootstrap-servers: 192.168.200.3:9092
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
consumer:
bootstrap-servers: 192.168.200.3:9092
group-id: my-group
auto-offset-reset: earliest
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer5. Implementing Kafka Producer and Consumer
Now that our configurations are set, we can create a producer to send messages and a consumer to listen for messages.
Step 1: Implement Kafka Producer
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafkaProducerService {
private static final String TOPIC = "my-topic";
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String message) {
this.kafkaTemplate.send(TOPIC, message);
log.info("Message sent: {}", message);
}
}Step 2: Implement Kafka Consumer
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafkaConsumerService {
@KafkaListener(topics = "my-topic", groupId = "my-group")
public void listen(String message) {
log.info("Received message: {}", message);
// Process the message
}
}Alternative using GSON
Developers can use the library for JSON serialization and deserialization to send a String (JSON) from a Kafka producer and consume it back as a JSON Object.
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.12.1</version>
</dependency>Define Order Model Object
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Order {
private String id;
private String status;
private int attemptCount;
private long lastAttemptTime;
private String payload;
}Kafka Producer (Convert Object to JSON String)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class OrderProducer {
private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
private final Gson gson;
public OrderProducer(KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate) {
this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;
this.gson = new Gson(); // Gson object for serialization
}
public void sendOrder(Order order) {
String jsonOrder = gson.toJson(order); // Convert object to JSON string
kafkaTemplate.send("my-topic", jsonOrder); // Send the JSON string to Kafka
}
}Kafka Consumer (Convert JSON String to Object)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Service
Slf4j
public class OrderConsumer {
private final Gson gson;
public OrderConsumer() {
this.gson = new Gson(); // Gson object for deserialization
}
@KafkaListener(topics = "my-topic", groupId = "my-group")
public void consume(String message) {
Order order = gson.fromJson(message, Order.class); // Convert JSON string to Order object
log.info("Received Order: {}", order);
}
}6. Exposing Kafka Producer via REST API
To allow external applications to send messages, we expose a REST API.
import com.example.programming.service.kafka.KafkaProducerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class KafkaController {
@Autowired
private KafkaProducerService producer;
@PostMapping("/publish")
public String publishMessage(@RequestParam("message") String message) {
producer.sendMessage(message);
return "Published successfully";
}
}7. Running and Testing Kafka Integration
Step 1: Start Kafka and Spring Boot Application
- Ensure Kafka is running.
- Run the Spring Boot application with Docker Compose:
dockerfile
# Stage 1: Build the application with Maven FROM maven:3.9.9-amazoncorretto-21 AS build # Set the working directory inside the container WORKDIR /app # Copy the pom.xml and src directory for building the app COPY pom.xml . COPY src ./src # Run Maven to clean and build the application (skip tests if needed) RUN mvn clean package -DskipTests # Stage 2: Create the final image to run the app FROM openjdk:21-jdk-slim # Set the working directory inside the container WORKDIR /app # Copy the built JAR file from the build stage COPY --from=build /app/target/*.jar app.jar # Expose the port the app will run on EXPOSE 8080 # Run the Spring Boot application ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "app.jar"]
docker-compose.yml
services:
spring-boot-app:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: spring-boot-container
ports:
- "8080:8080" # Map the container port to the host port
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: docker # Use the "docker" profile for Spring Boot (optional)
volumes:
- ./logs:/app/logs # Bind a volume for application logs (optional)
networks:
- kafka-server_kafka-network
networks:
kafka-server_kafka-network:
external: trueRun docker-compose
>docker compose up -d
Step 2: Send a Message via REST API
Use Postman or CURL:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/publish?message=HelloKafka"
Step 3: Check Kafka Consumer Output
The consumer should print:
Message sent: HelloKafka Received message: HelloKafka
8. Using JSON with Kafka
For sending JSON objects, modify your serializers and create model classes:
Define Kafka Configuration in application.yml
kafka:
producer:
bootstrap-servers: 192.168.200.3:9092
key-serializer: "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"
value-serializer: "org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonSerializer"
consumer:
bootstrap-servers: 192.168.200.3:9092
group-id: my-group
auto-offset-reset: earliest
key-deserializer: "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"
value-deserializer: "org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer"
properties:
spring.json.trusted.packages: "*"Implement Kafka Producer
import com.example.programming.model.Order;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafkaProducerService {
private static final String TOPIC = "my-topic";
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, Order> kafkaTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String message) {
Order order = new Order("001", "A", 1, 1, message);
this.kafkaTemplate.send(TOPIC, order);
log.info("Message sent: {}", message);
}
}Implement Kafka Consumer
import com.example.programming.model.Order;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafkaConsumerService {
@KafkaListener(topics = "my-topic", groupId = "my-group")
public void consume(Order order) {
log.info("Received Order: {}", order);
}
}Implement Bean
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Order implements Serializable {
private String id;
private String status;
private int attemptCount;
private long lastAttemptTime;
private String payload;
}Running and Testing Kafka using JSON
Run docker-compose
>docker compose up -d
Send a Message via REST API
Use Postman or CURL:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/publish?message=Hello"
Check Kafka Consumer Output
The consumer should print:
Message sent: HelloKafka Received Order: Order(id=001, status=A, attemptCount=1, lastAttemptTime=1, payload=Hello)
9. Best Practices for Kafka Integration
1. Use Proper Error Handling
Implement retries, logging, and dead-letter queues for failed messages.
2. Optimize Consumer Performance
- Use multiple partitions and consumer groups for scalability.
- Enable batch processing when consuming high-traffic topics.
3. Secure Kafka Communication
- Enable SSL/TLS for secure data transmission.
- Use authentication and authorization (SASL, ACLs).
4. Monitor Kafka Performance
Use tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Kafka Manager to monitor message flow and broker health.
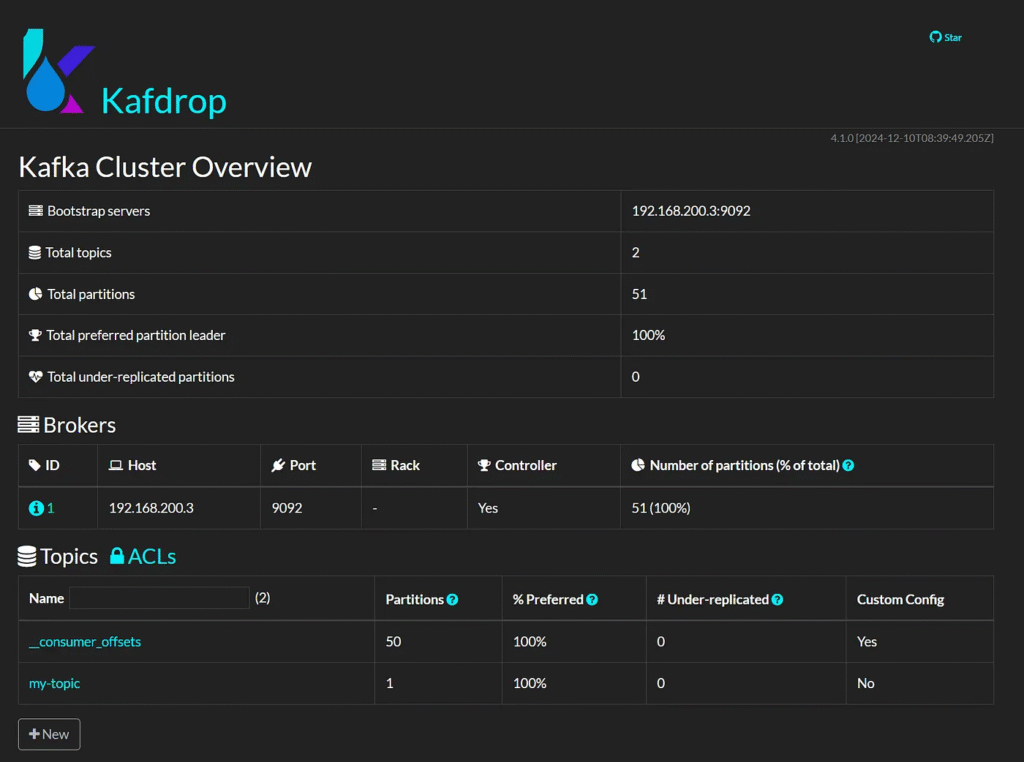
10. Monitoring with Kafdrop
Dashboard
http://localhost:9000/
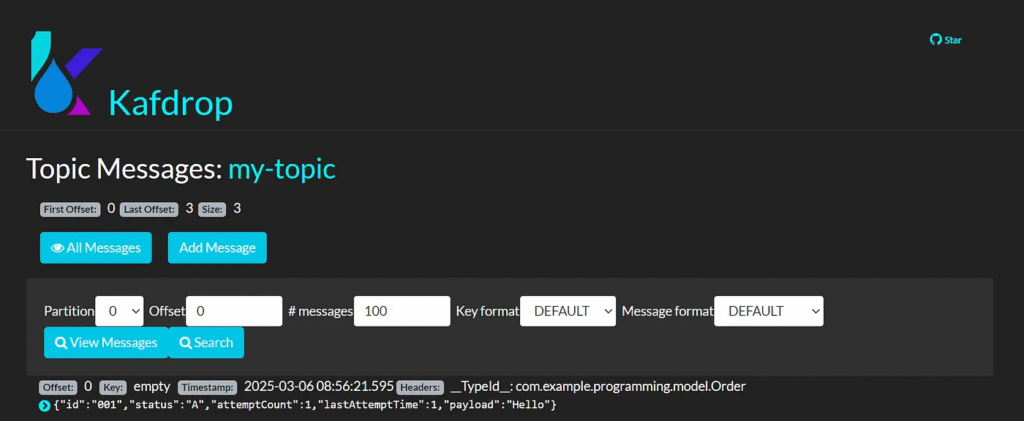
View Topic
my-topic

View messages
Conclusion
Spring Boot provides an easy and efficient way to integrate with Apache Kafka, enabling real-time data streaming in microservices and event-driven applications. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can set up a producer-consumer architecture with Kafka and Spring Boot, ensuring reliable messaging between distributed systems.
This article was originally published on Medium.




