Effective error handling is essential in modern web development. In Next.js, handling errors properly helps maintain user trust, enhances user experience, and simplifies debugging. This guide explains how to manage errors in Next.js using practical techniques across both expected and unexpected scenarios.
Handling Expected Errors
Expected errors occur during normal application flow. These errors should be anticipated and gracefully managed. In Next.js, this often involves server functions, server components, and handling 404 errors.
Server Functions
Server functions such as API routes or server actions often interact with databases or external APIs. These are prone to fail due to invalid inputs or network issues.
To handle these errors:
export async function POST(req: Request) {
try {
const body = await req.json();
if (!body.name) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ error: 'Name is required' }), { status: 400 });
}
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ success: true }));
} catch (error) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ error: 'Server error' }), { status: 500 });
}
}This approach ensures users receive meaningful feedback rather than cryptic server failures.
Server Components
When working with server components, always validate data before rendering. If data is missing or invalid, redirect the user or render a fallback.
import { notFound } from 'next/navigation';
export default async function ProductPage({ params }) {
const product = await getProduct(params.id);
if (!product) notFound();
return <div>{product.name}</div>;
}By using notFound(), you direct the user to the built-in 404 page automatically.
Not Found Pages
Next.js automatically shows a 404 page for routes that don’t exist. For custom styling, create a not-found.tsx file in the /app directory:
export default function NotFound() {
return <h1>Oops! Page not found.</h1>;
}This maintains branding consistency and reassures users that they’re still on your site.
Handling Uncaught Exceptions
Despite your best efforts, some errors will be unanticipated. Uncaught exceptions can crash your app if they are not handled appropriately.
Try-Catch Blocks
Use try-catch to wrap risky operations. This applies to both server and client code.
try {
const res = await fetch('/api/data');
const data = await res.json();
} catch (err) {
console.error('Unexpected error:', err);
}Logging errors helps developers identify and fix bugs quickly.
Error Logging Services
To monitor production environments, integrate services like Sentry or LogRocket. They provide real-time insights and stack traces, aiding rapid debugging.
Nested Error Boundaries
Next.js supports nested error boundaries in the app directory using the error.tsx convention. This feature allows you to isolate errors to specific parts of your application.
How It Works
Each route segment can include an error.tsx file. When an error occurs within that segment, the corresponding boundary displays instead of crashing the entire app.
For example:
/app
/products
page.tsx
error.tsxerror.tsx:
'use client';
export default function ProductError({ error, reset }) {
return (
<div>
<h2>Something went wrong with products.</h2>
<button onClick={reset}>Try again</button>
</div>
);
}This modularity enhances user experience and application resilience.
When to Use
Use nested boundaries when working with external data (such as APIs or databases), user-generated content, or third-party components. It improves app reliability without affecting unrelated sections.
Global Error Handling
While nested boundaries localize error management, a global handler acts as your safety net.
App-Level Error Boundary
Place an error.tsx file at the root of the /app directory. This catches any uncaught error not handled elsewhere.
'use client';
export default function GlobalError({ error, reset }) {
return (
<html>
<body>
<h2>Something went seriously wrong.</h2>
<button onClick={reset}>Retry</button>
</body>
</html>
);
}This ensures a fallback experience even for unhandled critical failures.
Use Error Monitoring Tools
Pair global boundaries with tools like Sentry to automatically log stack traces. That way, even silent failures are recorded for later review.
Example: CandleCraze — A Handmade Candle Store Built with Next.js
CandleCraze is a fictional small online shop that sells handmade candles. It uses Next.js for both its frontend and backend. The app handles user navigation, product display, and order placement. Error handling is critical for managing missing product pages, API issues, and broken components.
folder structure
candlecraze/ ├── app/ │ ├── page.tsx # Home page │ ├── not-found.tsx # Custom 404 page │ ├── error.tsx # Global error boundary │ ├── products/ │ │ ├── [slug]/ │ │ │ ├── page.tsx # Individual product page │ │ │ ├── error.tsx # Product-specific error boundary │ │ │ ├── ErrorBoundary.tsx ├── app/ │ └── actions/ │ └── placeOrder.ts # Server action for order placement ├── components/ │ └── OrderForm.tsx ├── styles/ │ └── globals.css # Global styles ├── data/ │ └── products.json ├── .env.local # Environment variables ├── next.config.js # Next.js configuration ├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript configuration └── package.json
Handling Expected Errors in Server Functions
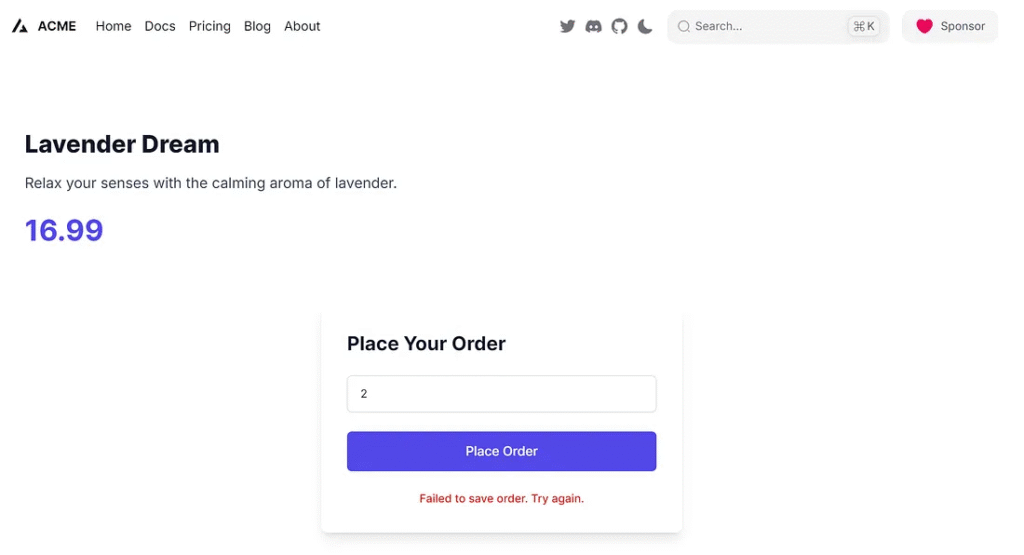
When users place an order, CandleCraze validates their input in a server action:
// /app/actions/placeOrder.ts
export async function placeOrder(data: FormData) {
const quantity = Number(data.get("quantity"));
if (!quantity) {
return { error: "Quantity are required." };
}
try {
if (quantity == 2) {
throw new Error();
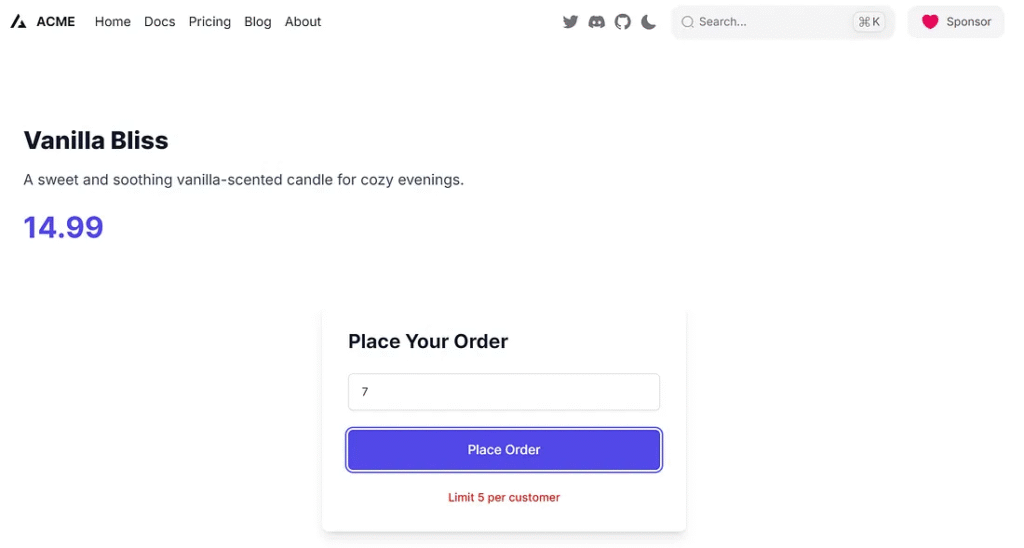
} else if (quantity > 5) {
return { error: "Limit 5 per customer" };
} else {
return { success: true };
}
} catch {
return { error: "Failed to save order. Try again." };
}
}Using Server Components and notFound()
If a user visits a product page for a candle that doesn’t exist, the app shows a 404 error:
// /app/products/[slug]/page.tsx
import { notFound } from "next/navigation";
import products from "../../../data/products.json";
import ErrorBoundary from "../ErrorBoundary";
import OrderForm from "@/components/OrderForm";
export async function findProductBySlug(slug: string) {
return products.find((product) => product.slug === slug) || null;
}
export default async function ProductPage({ params }: any) {
const product = await findProductBySlug(params.slug);
if (params.slug === "error-product") {
throw new Error("Simulated error: Product not found for ID " + params.slug);
}
if (!product) notFound();
return (
<ErrorBoundary>
<div>
<div className="px-6 py-8">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-extrabold text-gray-900 mb-4">
{product.name}
</h1>
<p className="text-lg text-gray-700 leading-relaxed mb-6">
{product.description}
</p>
<div className="flex items-center justify-between">
<strong className="text-4xl font-bold text-indigo-600 flex items-center">
{product.price}
</strong>
</div>
</div>
<OrderForm />
</div>
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}Order Form
// /app/products/[slug]/OrderForm.tsx
"use client";
import { useState } from "react";
import { placeOrder } from "@/actions/placeOrder";
export default function OrderForm() {
const [status, setStatus] = useState<string | null>(null);
async function handleSubmit(event: React.FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) {
event.preventDefault();
const formData = new FormData(event.currentTarget);
const result = await placeOrder(formData);
if ("error" in result) {
setStatus(result.error || "error");
} else {
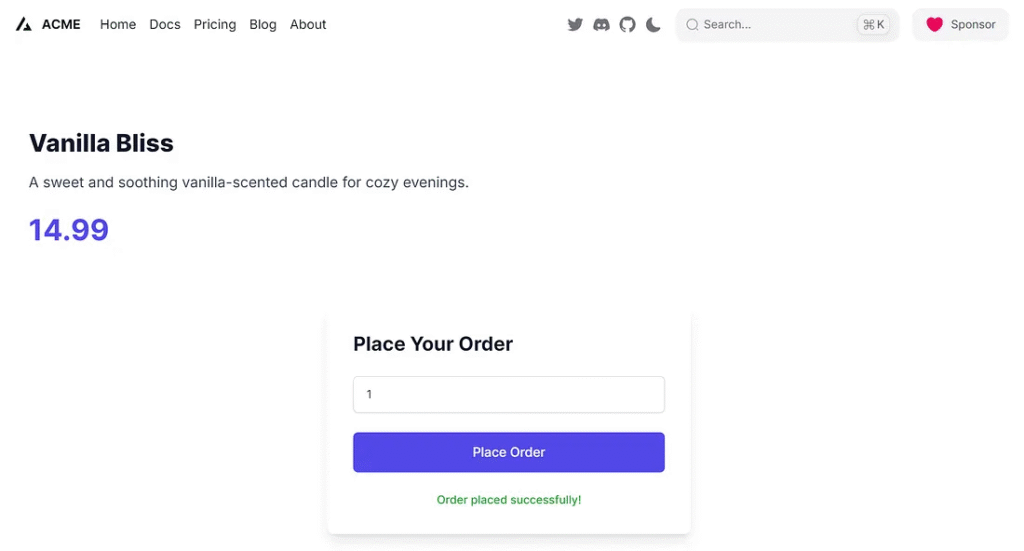
setStatus("Order placed successfully!");
}
}
return (
<div className="bg-white shadow-lg rounded-lg p-8 max-w-md mx-auto my-10">
<h2 className="text-2xl font-bold text-gray-900 mb-6 flex items-center">
Place Your Order
</h2>
<form className="space-y-6" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<div>
<label
className="block text-sm font-medium text-gray-700 sr-only"
htmlFor="quantity"
>
Quantity
</label>
<div className="mt-1">
<input
required
className="appearance-none block w-full px-4 py-3 border border-gray-300 rounded-md shadow-sm placeholder-gray-400 focus:outline-none focus:ring-indigo-500 focus:border-indigo-500 sm:text-sm"
id="quantity"
min="1"
name="quantity"
placeholder="Quantity"
type="number"
/>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<button
className="w-full flex justify-center py-3 px-4 border border-transparent rounded-md shadow-sm text-base font-medium text-white bg-indigo-600 hover:bg-indigo-700 focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-offset-2 focus:ring-indigo-500"
type="submit"
>
Place Order
</button>
</div>
{status && (
<p
className={`mt-4 text-center text-sm font-medium ${status.includes("successfully") ? "text-green-600" : "text-red-600"}`}
>
{status}
</p>
)}
</form>
</div>
);
}Custom 404 Page
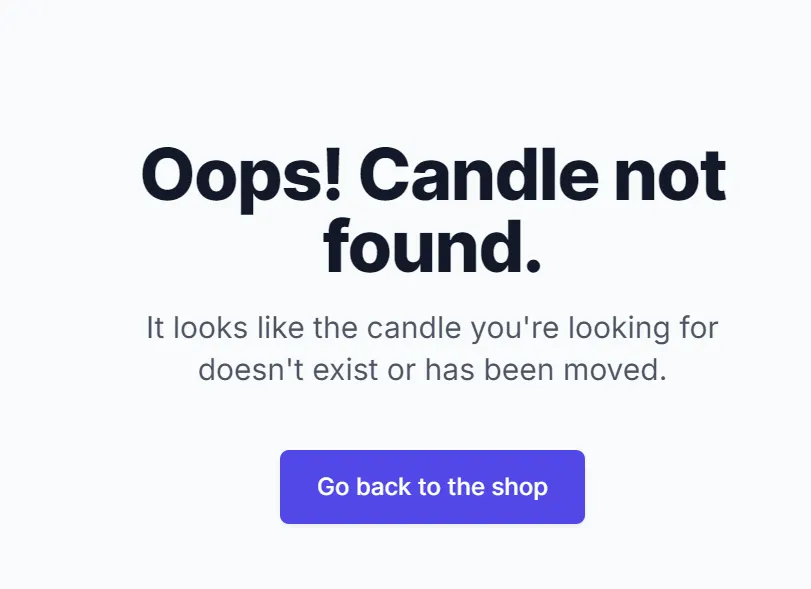
To maintain branding, CandleCraze uses a custom 404 page:
// /app/not-found.tsx
import Link from "next/link";
export default function NotFound() {
return (
<div className="min-h-screen flex flex-col items-center justify-center bg-gray-50 py-12 px-4 sm:px-6 lg:px-8">
<div className="max-w-md text-center">
<h1 className="mt-8 text-5xl font-extrabold text-gray-900 tracking-tight">
Oops! Candle not found.
</h1>
<p className="mt-4 text-xl text-gray-600">
It looks like the candle you're looking for doesn't exist or
has been moved.
</p>
<div className="mt-10">
<Link
className="inline-flex items-center px-6 py-3 border border-transparent text-base font-medium rounded-md shadow-sm text-white bg-indigo-600 hover:bg-indigo-700 focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-offset-2 focus:ring-indigo-500"
href="/"
>
Go back to the shop
</Link>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}Nested Error Boundaries for Products
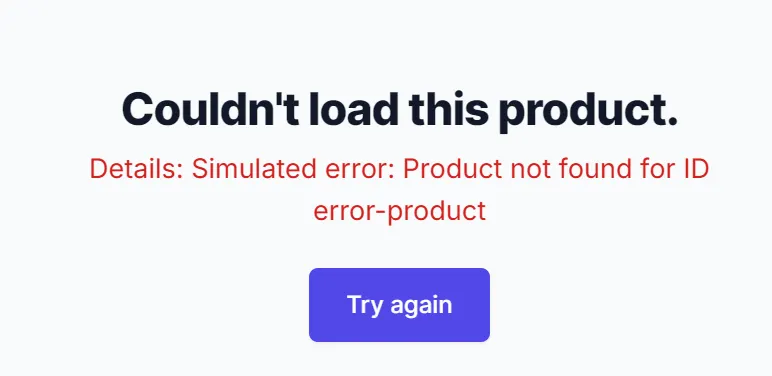
Each product has an error boundary to catch rendering issues:
"use client";
import { useEffect } from "react";
interface ProductErrorProps {
error: Error | null;
reset: () => void;
}
export default function ProductError({ error, reset }: ProductErrorProps) {
useEffect(() => {
console.error("Product error:", error);
}, [error]);
return (
<div className="min-h-screen flex flex-col items-center justify-center bg-gray-50 py-12 px-4 sm:px-6 lg:px-8">
<div className="max-w-md text-center">
<h2 className="mt-8 text-3xl font-extrabold text-gray-900 tracking-tight">
Couldn't load this product.
</h2>
{error && ( // Conditionally display the error message if 'error' is not null
<p className="mt-2 text-lg text-red-600">Details: {error.message}</p>
)}
<div className="mt-6">
<button
className="inline-flex items-center px-6 py-3 border border-transparent text-base font-medium rounded-md shadow-sm text-white bg-indigo-600 hover:bg-indigo-700 focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-offset-2 focus:ring-indigo-500"
onClick={reset}
>
Try again
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}"use client";
import React, { Component } from "react";
import ProductError from "./error"; // Assuming ProductError.tsx or .jsx is in the same directory
interface ErrorBoundaryProps {
children: React.ReactNode;
}
interface ErrorBoundaryState {
hasError: boolean;
error: Error | null;
}
class ErrorBoundary extends Component<ErrorBoundaryProps, ErrorBoundaryState> {
constructor(props: ErrorBoundaryProps) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false, error: null };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error: Error) {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
return { hasError: true, error: error };
}
componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: React.ErrorInfo) {
// You can also log the error to an error reporting service
console.error("ErrorBoundary caught an error:", error, errorInfo);
}
resetErrorBoundary = () => {
this.setState({ hasError: false, error: null });
};
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return (
<ProductError
error={this.state.error}
reset={this.resetErrorBoundary}
/>
);
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;Data
/data/products.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"slug": "vanilla-bliss",
"name": "Vanilla Bliss",
"description": "A sweet and soothing vanilla-scented candle for cozy evenings.",
"price": 14.99,
"image": "/images/vanilla-bliss.jpg"
},
{
"id": 2,
"slug": "lavender-dream",
"name": "Lavender Dream",
"description": "Relax your senses with the calming aroma of lavender.",
"price": 16.99,
"image": "/images/lavender-dream.jpg"
},
{
"id": 3,
"slug": "citrus-sunrise",
"name": "Citrus Sunrise",
"description": "A fresh citrus burst to energize your morning routine.",
"price": 13.99,
"image": "/images/citrus-sunrise.jpg"
}
]Global Error Boundary
A global fallback exists for all other routes:
"use client";
import { useEffect } from "react";
interface GlobalErrorProps {
error: Error;
reset: () => void;
}
export default function GlobalError({ error, reset }: GlobalErrorProps) {
useEffect(() => {
console.error("Global error caught:", error);
}, [error]);
return (
<>
<body>
<h2>Something went wrong with the shop.</h2>
<button onClick={reset}>Try again</button>
</body>
</>
);
}Run application
1. Run npm run dev
2. Visit http://localhost:3000
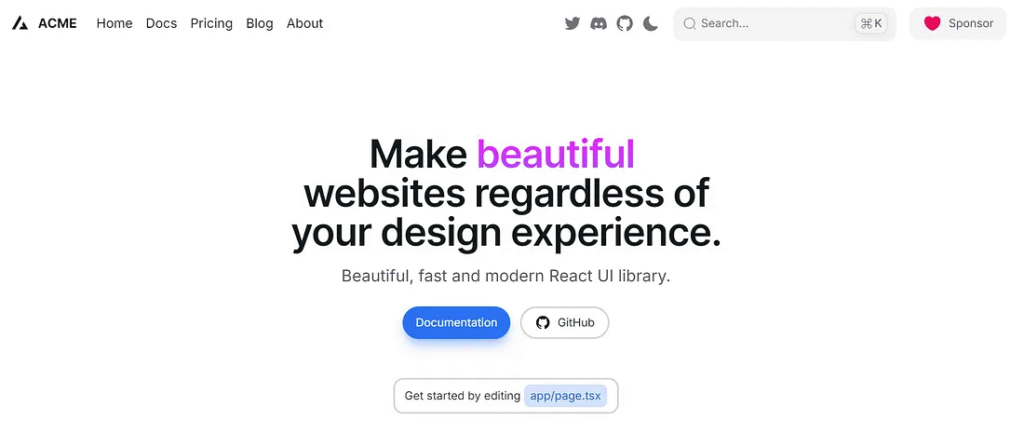
Product
http://localhost:3000/products/vanilla-bliss
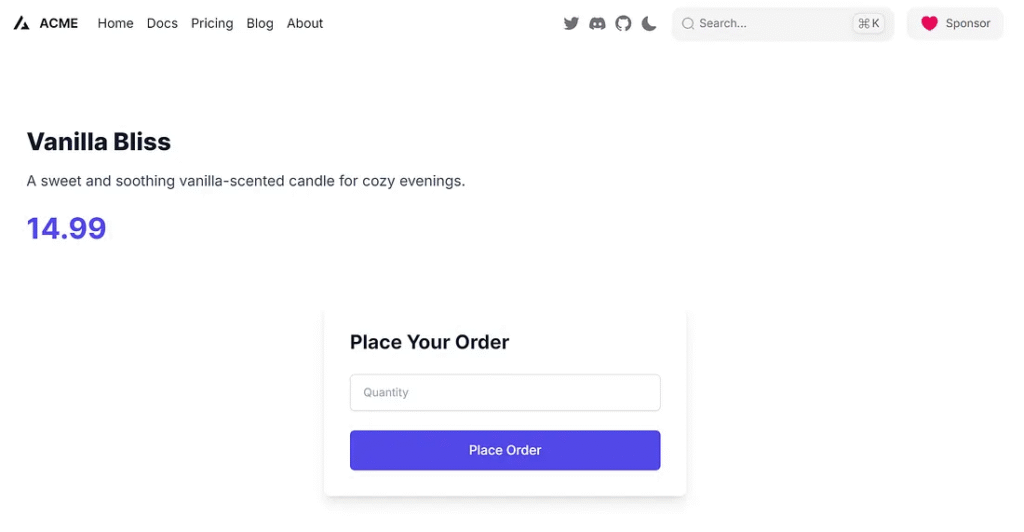
Place order
Product not found
http://localhost:3000/products/chocolate-bliss
Product error
http://localhost:3000/products/error-product
Conclusion
Error handling in Next.js is flexible and robust. Whether you’re catching expected errors in server functions, managing uncaught exceptions, or using nested and global error boundaries, Next.js equips you with tools to build resilient apps.
This article was originally published on Medium.



