Data flows faster than ever. Businesses receive information in endless formats — CSV, XML, JSON, or plain text. Yet, raw data rarely arrives in a ready-to-use form. Analysts spend hours cleaning, converting, and reshaping datasets. This wastes valuable time and slows decision-making.
Artificial intelligence changes the story. With AI, data transforms automatically, quickly, and accurately. AI not only converts formats but also builds meaningful summaries. Spring AI offers Java developers a powerful toolkit for this transformation journey. It combines Spring Boot’s reliability with AI’s adaptability.
When teams adopt AI for data tasks, they gain freedom. They stop worrying about formatting quirks and start focusing on insights. Every organization wants faster insights. Spring AI makes it possible without reinventing the wheel.
Not a Medium member? No problem! Read the full article here. Enjoy!
Introducing Spring AI
Spring AI extends the Spring Boot ecosystem. It provides simple interfaces for integrating AI models into Java applications. Developers can send prompts, process outputs, and plug AI into existing workflows.
Imagine needing a CSV-to-JSON converter. Traditionally, you would write parsers, handle exceptions, and cover edge cases. With Spring AI, you describe the task in natural language. The AI interprets the request and performs the necessary transformations.
Spring AI abstracts complexity. You gain high-level APIs that work with different AI providers—no need to hard-code logic for each format. Instead, you orchestrate a flow where AI handles unpredictable data structures.
In short, Spring AI enhances Java’s capabilities. It enhances traditional applications with flexible intelligence.
Setting Up the Project


Creating a Data Conversion Service
Let’s build a service that transforms CSV data into JSON. Start with a Spring @Service class:
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Objects;
@Service
public class DataTransformer {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public DataTransformer(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}
public String convertCsvToJson(String csvData) {
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Provide the output as plain text only. Convert this CSV into JSON: " + csvData);
return Objects.requireNonNull(chatClient.prompt(prompt).call().chatResponse()).getResult().getOutput().getText() ;
}
}This class defines a straightforward method. It accepts CSV input, prompts the AI, and returns JSON output. No custom parsing logic. No manual schema handling. AI handles it.
Building a REST Controller
Next, expose the service through a REST API. This allows external tools to send data for conversion.
import com.example.spring_ai.service.DataTransformer;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/transform")
public class DataController {
private final DataTransformer transformer;
public DataController(DataTransformer transformer) {
this.transformer = transformer;
}
@PostMapping("/csv-to-json")
public String transformCsv(@RequestBody String csvData) {
return transformer.convertCsvToJson(csvData);
}
}Now, developers can post CSV data to /transform/csv-to-json and receive JSON in return. This endpoint brings instant value. It saves hours of manual conversion effort.
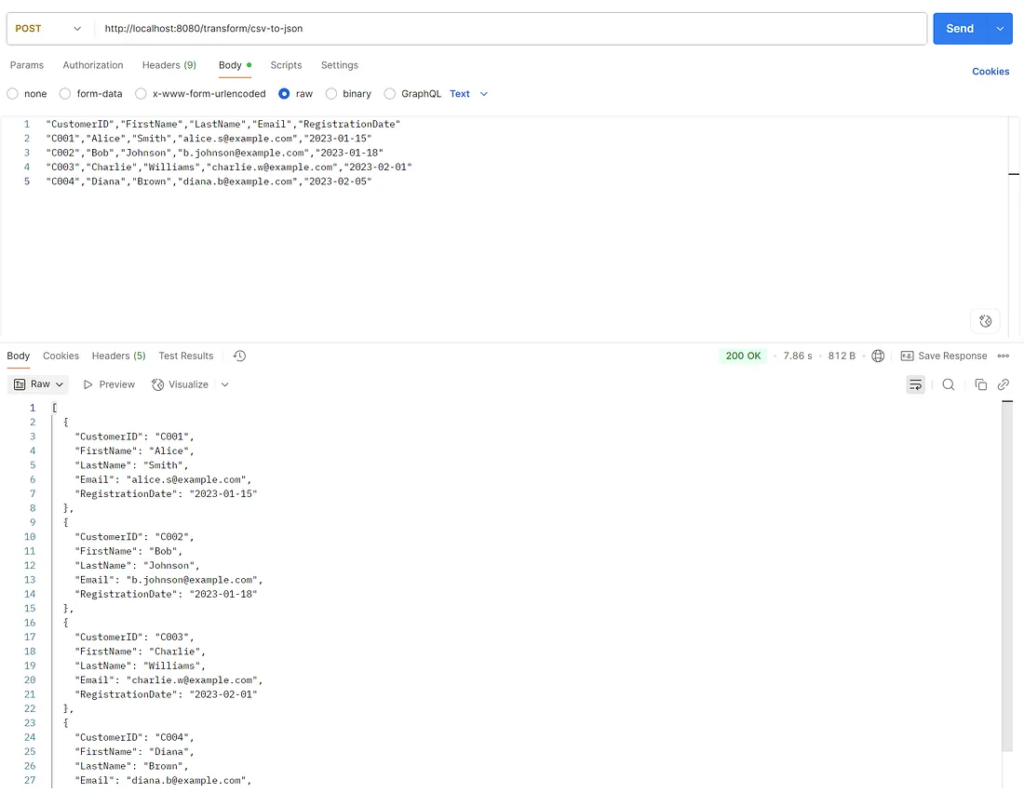
Example data.
"CustomerID","FirstName","LastName","Email","RegistrationDate" "C001","Alice","Smith","[email protected]","2023-01-15" "C002","Bob","Johnson","[email protected]","2023-01-18" "C003","Charlie","Williams","[email protected]","2023-02-01" "C004","Diana","Brown","[email protected]","2023-02-05"
Enhancing with Structured Summaries
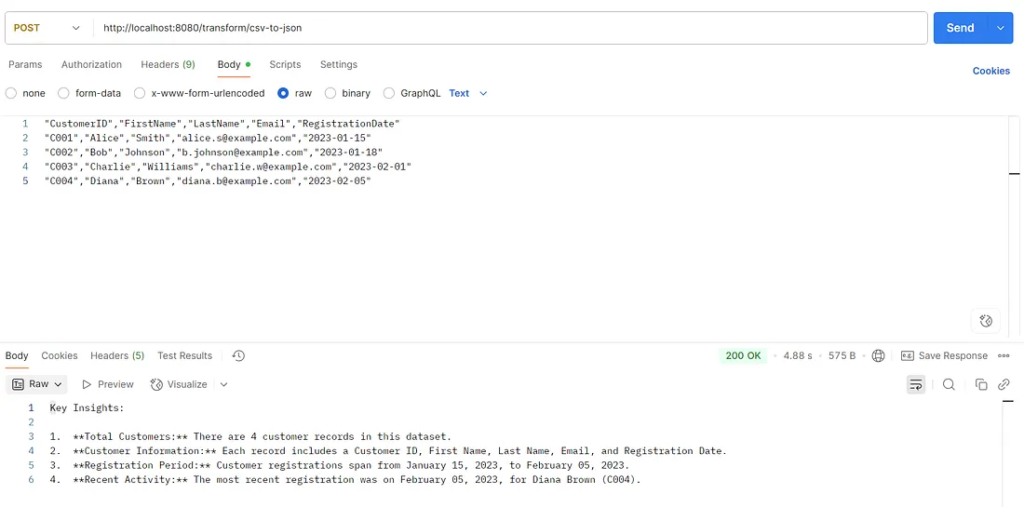
Beyond format conversion, AI can summarize data. Instead of raw JSON, you can request structured insights.
For example:
public String summarizeCsv(String csvData) {
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Summarize this CSV into key insights: " + csvData);
return chatModel.call(prompt).getResult().getOutput().getContent();
}This method generates summaries instead of strict conversions. It allows businesses to move from raw data to actionable insights instantly.
Benefits of Spring AI in Data Transformation
Spring AI reduces boilerplate code. Traditional conversion requires libraries, schema definitions, and error handling. AI eliminates many steps.
The framework integrates smoothly with Spring Boot. Developers already comfortable with Java will find it a natural fit. It offers flexibility. You can use it for structured conversions or creative tasks.
AI handles edge cases gracefully. If the CSV contains unexpected characters, AI adapts. This adaptability is hard to achieve with static parsers.
Most importantly, Spring AI saves time. Teams ship faster. They focus on innovation rather than repetitive formatting.
Expanding to Other Formats
Spring AI is not limited to CSV and JSON. It can handle XML, YAML, or plain text. Adding another method is simple:
public String convertXmlToJson(String xmlData) {
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Convert this XML into JSON: " + xmlData);
return chatModel.call(prompt).getResult().getOutput().getContent();
}This method works the same way. The AI interprets XML and produces JSON. Developers gain a universal transformation engine.
Handling Large Files
Large files can overwhelm AI models. To handle them, split the data into chunks. Process each chunk separately. Then merge the results into a final structure.
Spring provides streaming capabilities. Combine them with AI to create pipelines. This ensures scalability while maintaining accuracy.
Practical Use Cases
Businesses can apply this approach across industries:
- Finance: Transform transaction logs into structured summaries.
- Healthcare: Convert patient records into standardized formats.
- Retail: Summarize customer feedback into actionable insights.
- Education: Reformat student performance data for reports.
Each case saves time and unlocks hidden insights.
Practical Use Case Finance
This example demonstrates how to use Spring AI with mock data to summarize raw financial transactions.
1. The Structured Data Model
First, define a Java record to represent the desired summary. This record acts as a blueprint for the AI’s output, instructing it on the exact structure (fields, data types) to return.
// src/main/java/com/example/finance/TransactionSummary.java
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Represents a structured summary of financial transactions.
* @param totalExpenses The total amount of all transactions.
* @param expensesByCategory A map of category to total expense amount.
* @param summary A concise, human-readable summary of the transactions.
*/
public record TransactionSummary(
double totalExpenses,
Map<String, Double> expensesByCategory,
String summary
) {}2. The Service with Spring AI
This service class uses the ChatClient to interact with an AI model. It prepares the mock data and a PromptTemplate to guide the AI, then uses the BeanOutputConverter to process the AI’s response.
// src/main/java/com/example/finance/FinancialAnalysisService.java
package com.example.finance;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.PromptTemplate;
import org.springframework.ai.parser.BeanOutputConverter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class FinancialAnalysisService {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
// Mock data representing unstructured transaction logs.
private static final List<String> MOCK_TRANSACTION_LOGS = List.of(
"Card purchase at Amazon.com for $52.99 on 2025-09-24.",
"Transfer to Jane Doe for $200.00 on 2025-09-23.",
"Uber ride costing $15.50 on 2025-09-22.",
"Grocery store visit at FreshMart for $85.75 on 2025-09-21.",
"Netflix subscription payment of $14.99 on 2025-09-20."
);
public FinancialAnalysisService(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}
public TransactionSummary analyzeTransactions() {
// Join mock logs into a single string to send to the AI.
String transactionLogs = MOCK_TRANSACTION_LOGS.stream()
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
// Create a converter for our TransactionSummary record.
var outputConverter = new BeanOutputConverter<>(TransactionSummary.class);
// Define a prompt with instructions and placeholders for the data.
String promptText = """
Analyze the following transaction logs and provide a structured summary.
Include the total expenses, a breakdown of expenses by category, and a brief overall summary.
Transaction Logs:
{logs}
{format}
""";
// Use a PromptTemplate to dynamically insert the data and format instructions.
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(promptText);
// Build the prompt and call the AI model.
// The .entity() method automatically applies the converter and
// returns the data as a TransactionSummary object.
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(promptTemplate.create(Map.of(
"logs", transactionLogs,
"format", outputConverter.getFormat()
)))
.call()
.entity(TransactionSummary.class);
}
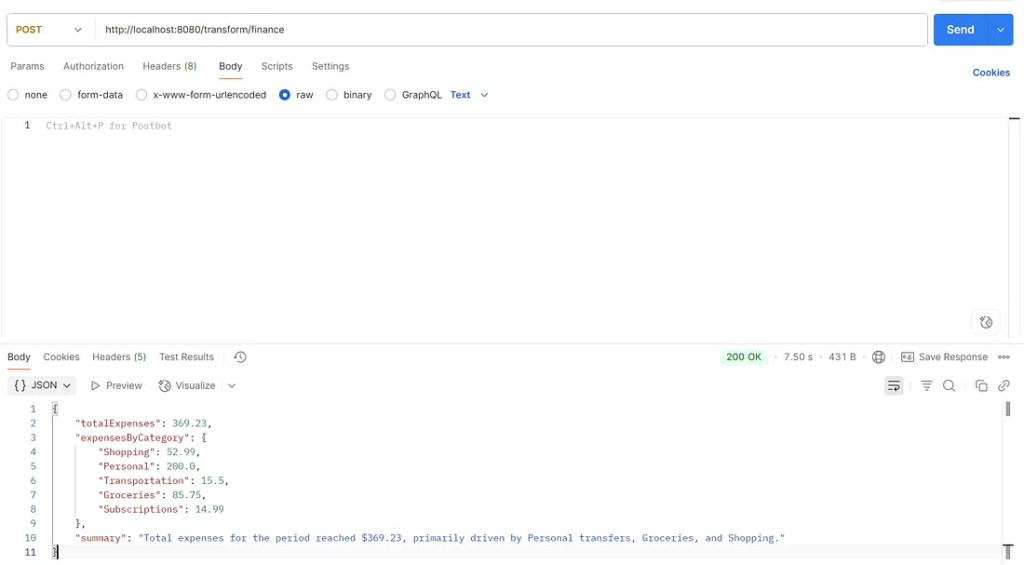
}3. Example Output (Simulated)
While the exact AI output will vary, the BeanOutputConverter guarantees it will conform to the TransactionSummary record’s structure. Here’s a likely JSON response from the AI that Spring AI would then convert into the Java object:
{
"totalExpenses": 369.23,
"expensesByCategory": {
"Shopping": 52.99,
"Personal": 200.0,
"Transportation": 15.5,
"Groceries": 85.75,
"Subscriptions": 14.99
},
"summary": "Total expenses for the period reached $369.23, primarily driven by Personal transfers, Groceries, and Shopping."
}
Best Practices for Reliable Transformation
AI output can vary. To improve reliability:
- Define clear prompts.
- Test with diverse datasets.
- Post-process results with validation checks.
- Log conversions for audit purposes.
These practices ensure consistent, trustworthy outcomes.
Scaling with Microservices
Deploying the transformation service as a microservice adds flexibility. Each microservice can handle a different format—for example, one for CSV, another for XML.
Spring Boot supports containerization with ease. Deploy services with Docker and orchestrate them with Kubernetes. Scaling becomes effortless.
Security Considerations
Never expose raw API keys in code. Store them securely in environment variables. Use HTTPS for all data transfers. Sensitive data should be masked or anonymized before processing.
Compliance is crucial in industries such as healthcare and finance. Always align with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Inspiring the Developer Mindset
AI-powered transformation frees developers from repetitive work. It inspires creativity. Developers can design more intelligent workflows, automate reporting, and enrich customer experiences.
Spring AI empowers Java developers to shape the future. Data becomes a resource, not a roadblock. Every project gains speed and adaptability.
Future of Data Transformation with AI
Tomorrow’s systems will rely on instant, AI-driven transformation. Teams will no longer write complex parsing code. Instead, they will describe desired outcomes, and AI will deliver.
Spring AI positions developers to lead this change. By learning it today, they prepare for tomorrow’s data challenges.
Finally
Data transformation no longer needs to be tedious. With Spring AI, Java developers convert, summarize, and enrich data seamlessly.
Start with a simple CSV-to-JSON service. Then expand to summaries, XML, and beyond. Keep best practices in mind. Secure your data. Scale with microservices.
The journey begins with a single line of code and a clear vision. Use Spring AI to unlock the power of intelligent transformation. The future of data is waiting.
This article was originally published on Medium.



